Understanding the significance of breakfast takes on a new dimension when considering its impact on individuals with Type 2 diabetes. Dubbed the most crucial meal of the day, its value escalates for those managing this condition due to its profound effects on daily well-being and blood sugar regulation, underscoring the need for a good Indian diet for diabetes and diet management for Type 2 diabetes.
The Science Behind Breakfast and Blood Sugar Levels
Initiating your day with a nourishing breakfast is pivotal for an energy boost and stabilizing blood glucose levels. The research underscores the importance of a morning meal in enhancing insulin sensitivity, which tends to be more pronounced during the early hours. This fact is especially crucial in diabetes type 2 breakfast recipes, highlighting the significance of a good breakfast for Type 2 diabetes. Contrary to the common query, breakfast does not directly lower blood sugar. However, the strategic selection of food groups—balancing proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates—plays a vital role in maintaining glycemic control, thus energizing the body and averting abrupt spikes or drops in blood sugar, which is key in healthy breakfast Type 2 diabetes management.
Optimal Timing for Breakfast
For optimal health outcomes, individuals with diabetes are advised to consume breakfast within an hour and a half of waking. This practice, integral to the best breakfast Type 2 diabetes strategy, is part of a broader approach to eating meals at consistent times each day, helping to keep blood sugar levels within a desirable range and minimizing the risks of volatility.
Dietary Considerations for Type 2 Diabetes
The composition of the breakfast plate is as critical as its timing, aligning with the Indian Type 2 diabetes diet. Incorporating a variety of nutrients—proteins, unrefined whole grains, vegetables, and fruits—enhances dietary balance. However, a noteworthy piece of advice for those with Type 2 diabetes is to moderate the intake of fruits during breakfast or to alternatively enjoy them as snacks between meals to avoid potential blood sugar spikes, an essential aspect of the Indian vegetarian diet for Type 2 diabetes.
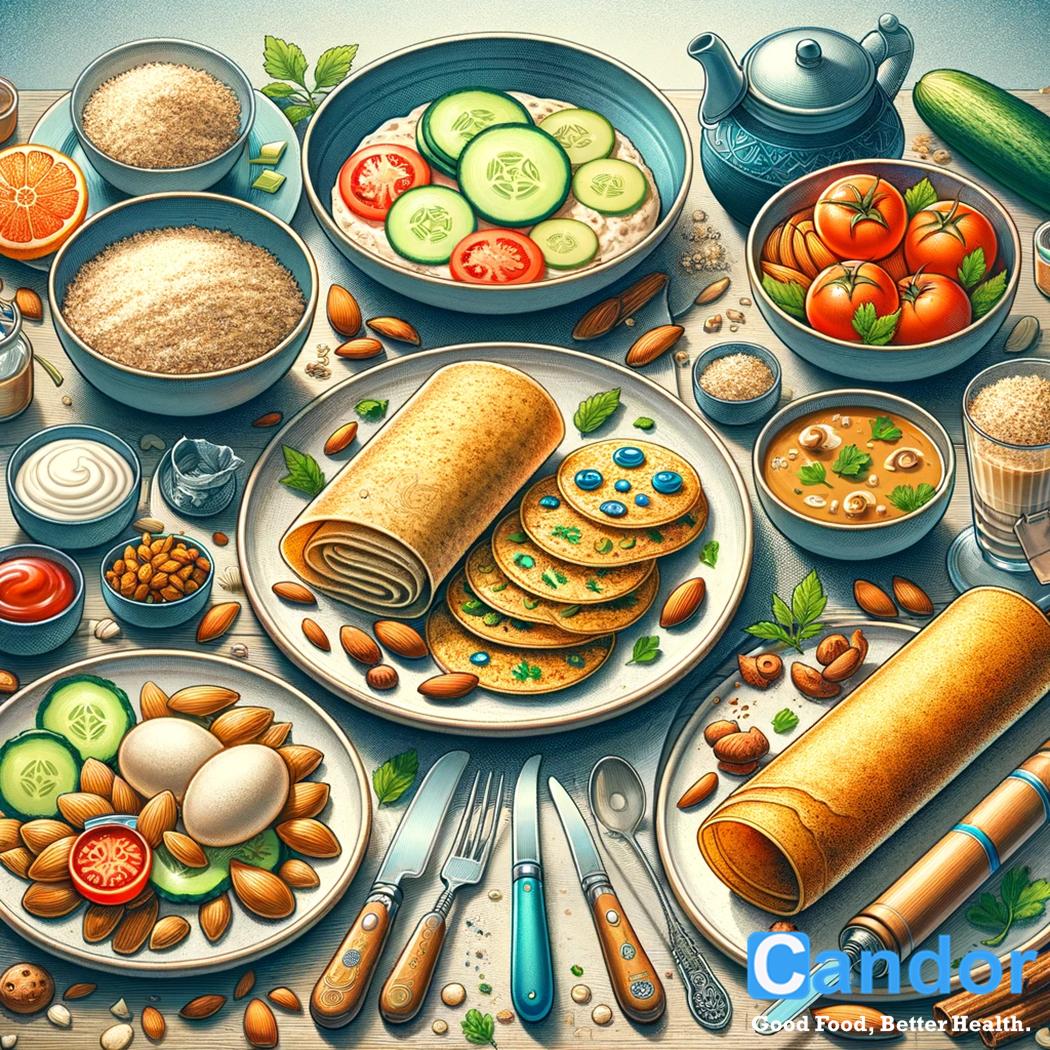
Tailoring Breakfast to Suit Indian Dietary Preferences
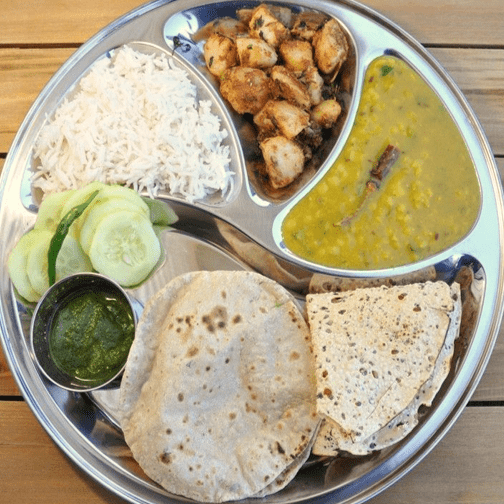
For those inclined towards Indian cuisine, the breakfast table offers many options that align well with diabetic dietary needs, making it a prime example of a type 2 diabetes Indian food list. Traditional Indian ingredients like eggs, low-fat paneer, sprouts, unpolished grains, and vegetables and nuts form the cornerstone of a diabetic-friendly breakfast, fitting into the type 2 diabetes Indian diet.
Emphasizing proteins from sources like paneer, lentils, and eggs, alongside whole grains such as ragi and oats, can significantly contribute to a balanced and nutritious start to the day, showcasing the diabetes type 2 breakfast cereals and overall meal planning crucial for managing this condition effectively.
Strategies for a Diabetes-Friendly Breakfast
- Achieve a Balanced Plate: Prioritize a mix of macronutrients to ensure sustained blood sugar levels.
- Prefer Low Glycemic Index Foods: Foods like barley, millet, chickpeas, and lentils are excellent for a gradual glucose release.
- Incorporate Healthy Fats and Proteins: Options like nuts, seeds, and lean proteins support satiety and metabolic health.
- Fiber is Key: Fiber-rich foods aid in digestion and glucose control.
- Mindful Portions: Be aware of serving sizes to prevent unintended blood sugar increases.
- Avoid High-Sugar and Refined Foods: These can lead to rapid glucose spikes.
- Stay Hydrated: Begin your day with water, adding unsweetened beverages as preferred.
- Plan Ahead: For hectic mornings, prepare manageable breakfast options in advance.
- Monitor Glucose Responses: Understanding personal glucose triggers is crucial for dietary adjustments.
- Seek Professional Guidance: A dietitian can offer tailored advice to meet individual health goals.
Common topics for Indian breakfast options for diabetics
- Best Indian Breakfast Options: Nutrient-rich dishes like oats upma and moong dal cheela are recommended.
- Coconut Chutney: While low in GI, moderation is key due to its potential impact on blood sugar levels.
- Meal Skipping: Not advisable as it can disrupt blood sugar control and appetite regulation.
- Sabudana: Best consumed in moderation, balanced with low glycemic and high-fiber foods.
- Weight Management with Poha: When prepared with minimal oil and high-fiber ingredients, it can support weight loss.
- Making Indian Breakfast Healthier: Emphasize whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins while limiting oil use.
- Idli for Diabetes: Opt for whole-grain versions and pair them with protein-rich sambhar for a balanced meal.
- Ideal Breakfast Composition: High in fiber and protein; low in processed sugars and unhealthy fats.
- Sweet Breakfast Options: Opt for natural sweeteners and maintain portion control.
- Vegetarian and Vegan Considerations: Many Indian breakfasts are adaptable to these dietary preferences.
- Smoothies: A balanced mix of ingredients can make smoothies a healthy addition to breakfast.
Embracing these insights into breakfast planning can markedly improve daily management of Type 2 diabetes, contributing to overall health and well-being.
References:
- Sharma, P., Gupta, S., & Kumar, A. (2023). “Evaluating the Glycemic Index of Traditional Indian Breakfasts in Type 2 Diabetes Management.” Journal of Diabetic Nutrition and Metabolic Research.
- Patel, M., Singh, J., & Mehta, D. (2022). “Protein-Rich Indian Breakfasts and Their Impact on Blood Glucose Levels in Type 2 Diabetics.” Nutrition and Diabetes Care Journal.
- Kumar, R., Venkataraman, S., & Lakshmi, T. (2021). “A Comparative Study of Whole Grain and Refined Grain Breakfasts on Glycemic Control in Type 2 Diabetics.” International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.
- Joshi, S., & Agarwal, M. (2020). “The Role of Fiber-Rich Indian Breakfasts in the Dietary Management of Type 2 Diabetes.” Journal of Nutrition and Diabetes Research.