In the realm of diabetes management, technological innovations have emerged as invaluable assets, providing a myriad of solutions to effectively control blood sugar levels, especially in the context of type 2 diabetes. This comprehensive tech guide for diabetes delves into a spectrum of cutting-edge technologies that individuals can leverage to navigate the intricacies of diabetes management, offering not only enhanced control but also avenues for communal support.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Elaboration: Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) stands as a pinnacle of wearable technology, a sophisticated apparatus designed to provide real-time insights into glucose levels. Implanted beneath the skin, typically in the arm or belly, this technological marvel tirelessly monitors glucose fluctuations around the clock. The continuous data stream offers a holistic perspective, allowing individuals to discern patterns and trends in their blood sugar levels. By capturing the nuances of how glucose levels rise and fall throughout the day, CGM empowers users with the knowledge needed to make timely adjustments, ultimately contributing to a more nuanced and effective diabetes management strategy.
In-Depth Features:
- Alarms strategically alert users to deviations in glucose levels.
- Seamless integration with factors influencing blood sugar, such as exercise, food intake, and medications.
- Data accessibility through smartphones or computers facilitates a comprehensive review.
Cost Considerations: While the cost of CGM devices varies among brands, it’s noteworthy that Medicare may extend coverage based on specific qualifying criteria, offering a potential avenue for financial relief.
Insulin Pump
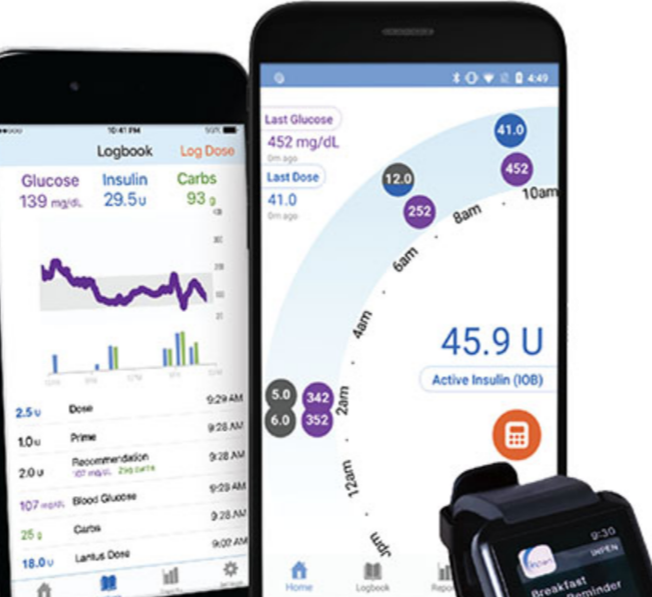
Examination: The insulin pump emerges as a sophisticated computerized companion in the quest for stable blood sugar levels. This compact device, intricately connected to the body, ensures a continuous supply of insulin, mitigating the risk of sudden spikes or dips in blood sugar. With various attachment options, including tubing or disposable patches, the insulin pump epitomizes technological precision in diabetes care.
Enhanced Integration with CGM: The synergy between CGM and insulin pumps is a hallmark of advanced diabetes management. The data gleaned from CGM usage can be seamlessly integrated into insulin pump programming, optimizing insulin delivery throughout the day. This harmonious collaboration significantly reduces the risks associated with erratic blood sugar levels, offering users a more streamlined and effective approach to diabetes control.
Financial Facet: Insurance coverage, which may extend up to 80–90% of total costs for qualifying individuals, positions insulin pumps as accessible aids in diabetes management.
Glucometers
Insightful Examination: Glucometers, commonly known as blood glucose monitors, stand as stalwart companions in the daily routine of diabetes management. These compact devices, requiring only a small blood sample obtained through a simple finger prick, provide instantaneous readings of blood sugar levels.
Evaluating Cost Effectiveness: While the initial investment in a glucometer is relatively modest, the recurring expenses associated with test strips can accumulate, ranging from $1000 to $3000 annually. However, individuals covered under Medicare Part B can find solace in the coverage, mitigating potential out-of-pocket expenses.
Insulin Pens
Comprehensive Analysis: Insulin pens, both reusable and disposable, offer a manual yet convenient means of insulin delivery. These pens, containing vials or cartridges of insulin, empower individuals to self-administer insulin injections with ease, especially when on the go.
Evolution into Smart Insulin Pens: The evolution of insulin pens into smart devices heralds a new era in diabetes management. These intelligent pens, often accompanied by companion apps, transcend mere insulin delivery. They boast features such as dose calculation based on real-time glucose levels, dose tracking, reminders for insulin replacement, and seamless communication of diabetes-related data to healthcare providers.
Navigating Financial Realities: While insulin pens and insulin fall outside the coverage purview of Medicare Part B, Medicare Part D steps in to cover the costs of injectable insulin used in conjunction with a pen. Notably, the investment in managing diabetes with insulin pens may incur a monthly cost exceeding $100 for those without insurance coverage.
Smartphone Apps
Strategic Deployment: Smartphone apps emerge as indispensable allies in the multifaceted landscape of diabetes management. These applications, designed to track and record various facets of daily life, including food consumption, exercise routines, blood glucose levels, medications, and carbohydrate intake, offer a comprehensive overview.
Synergistic Role: While not designed as standalone monitoring systems for blood glucose levels, these apps play a synergistic role in tandem with other monitoring devices. Their versatility allows users to choose an app tailored to their specific needs, providing an additional layer of convenience in managing various aspects of diabetes.
The fusion of technology and diabetes management is not merely a convergence of devices; it represents a paradigm shift in how individuals approach their health. Beyond the realms of data tracking and insulin delivery, it encapsulates a journey of connectivity, support, and empowerment. As technology continues to evolve, so does the narrative of living with type 2 diabetes, transforming it into a tale of resilience, community, and the boundless possibilities that arise when human tenacity meets technological innovation.
Telemedicine
Transformative Approach: Telemedicine, a revolutionary paradigm in healthcare, transcends geographical constraints by delivering medical care remotely, either over the phone or through online platforms. In the realm of diabetes management, telemedicine serves as a consistent source of support, offering ongoing assistance to individuals navigating their treatment plans.
Economic Considerations: Beyond the realm of health benefits, telemedicine presents a compelling economic case by eliminating the need for in-office visits. Research indicates that both patients and healthcare providers stand to accrue financial savings, especially in the context of screening for complications associated with diabetes, such as diabetic retinopathy.
Online Communities
Community Dynamics: Acknowledging the emotional and psychological dimensions of managing type 2 diabetes, online communities emerge as dynamic ecosystems fostering connection and support. These virtual spaces, encompassing forums, blogs, videos, podcasts, social media platforms, and support groups, transcend geographical boundaries, providing a haven for shared experiences.
Multi-Faceted Benefits: Beyond the exchange of knowledge, these online communities serve as hubs for local and global advocacy, self-expression, and even humor. Recognizing the importance of humor and joy in navigating the challenges of diabetes, these platforms become not just information repositories but also outlets for coping mechanisms.
Financial Accessibility: Participation in these online communities is inherently free, ensuring accessibility for individuals seeking a supportive network without financial barriers.
Coping With Type 2 Diabetes
Holistic Reflection: As individuals embark on the journey of coping with type 2 diabetes, the amalgamation of technological solutions assumes a transformative role. The seamless integration of smart insulin pens, continuous glucose monitoring systems, glucometers, insulin pumps, smartphone apps, telemedicine, and online communities paints a holistic canvas of support.
Empowering Through Connectivity: Embracing technology transcends the mere management of blood sugar levels; it empowers individuals to live more freely and proactively engage in their health journey. The collaborative approach, where real-time data informs decisions, not only streamlines diabetes control but also fosters a sense of agency and empowerment.
Embracing the Lengthy Tapestry of Technology: In navigating the expansive landscape of diabetes management, the lengthier tapestry woven by these technological advancements stands as a testament to human ingenuity. From the intricacies of continuous glucose monitoring to the transformative potential of telemedicine and the communal strength drawn from online platforms, each thread contributes to a comprehensive and nuanced approach to coping with type 2 diabetes.
References:
- Bashier A, Bin Hussain A, Abdelgadir E, Alawadi F, Sabbour H, Chilton R (2019). “Consensus recommendations for management of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular diseases”. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. Continuous glucose monitoring.
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee (January 2019). “Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2019”. Diabetes Care.
- Medicare. Blood sugar monitors.
- Mullur RS, Hsiao JS, Mueller K. (2022) “Telemedicine in diabetes care.” American Family Physician.