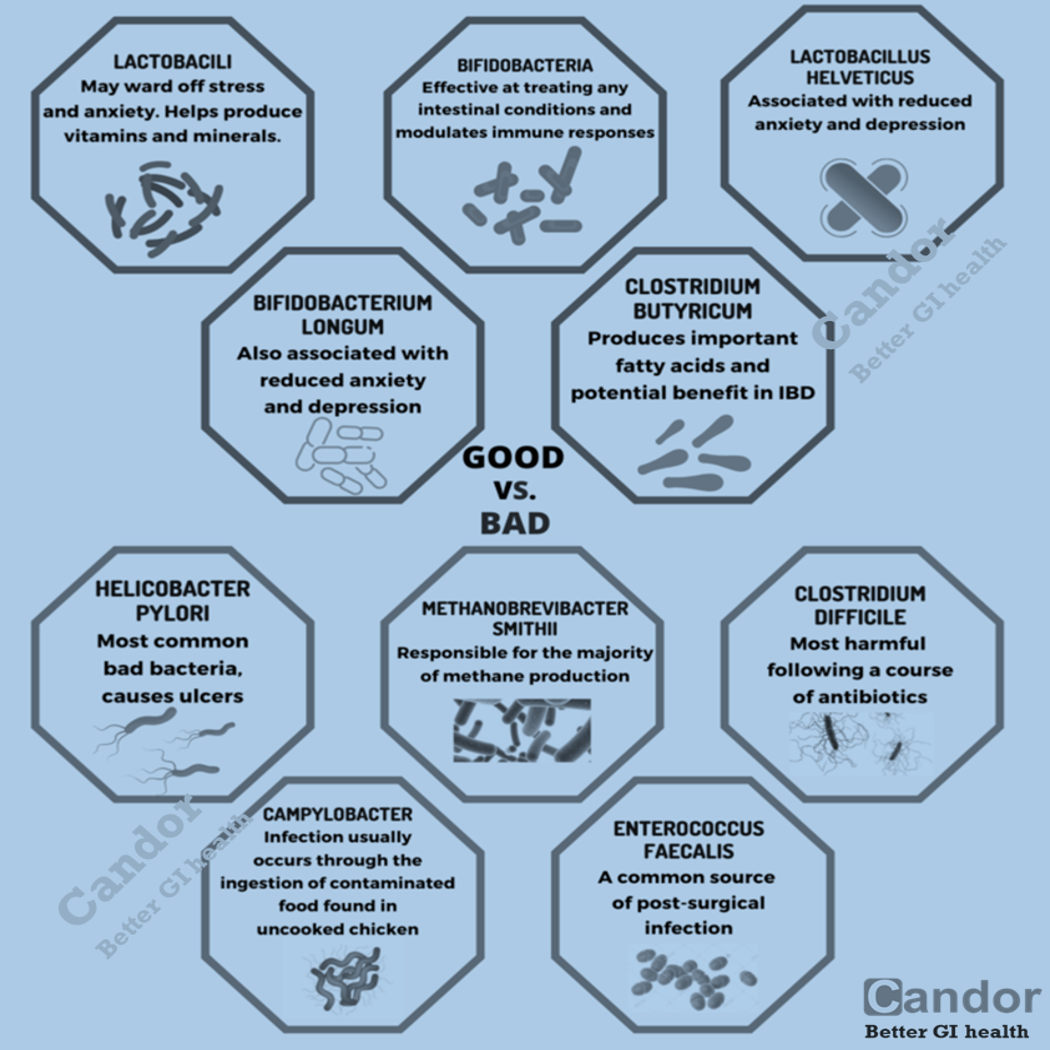
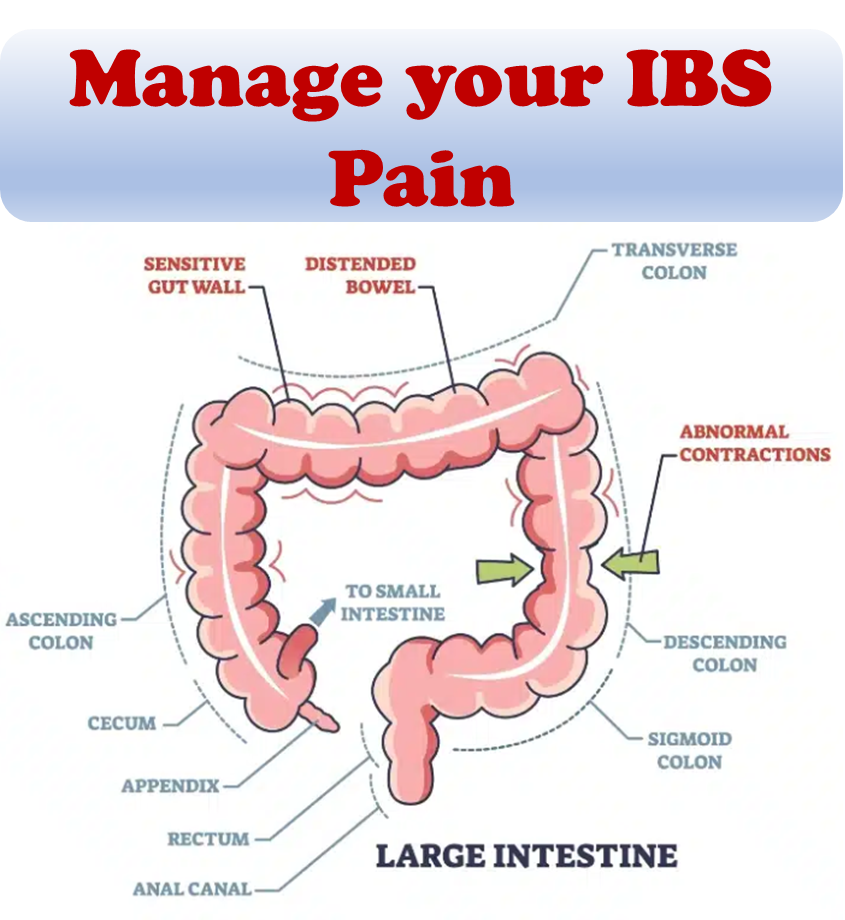
How do Doctors Perform Colonoscopy?
For the procedure, you’ll lie on a table while the doctor inserts a colonoscope through your anus and into your rectum and colon. The scope inflates your large intestine with air for a better view. The camera sends a video image to a monitor, allowing the doctor to examine your large intestine.
References:
1. NIH
2. NIDDK
Join the conversation at https://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp