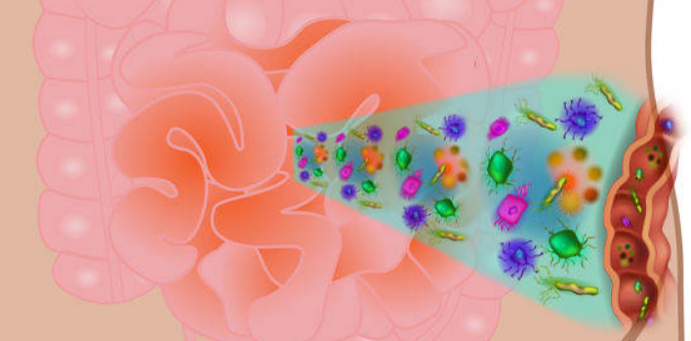
The gut barrier is our first line of defense against harmful microbes in the GI tract. Its role in maintaining health and its contribution to immune response is an active topic of research.
What is the gut barrier?
The intestine normally exhibits some permeability, which allows nutrients to pass through the gut, while also maintaining a barrier function to keep potentially harmful substances (such as antigens) from leaving the intestine and migrating to the body more widely. The gut barrier (formed by the intestinal epithelium) is an extremely important mucosal surface and separates the external environment (present in the intestinal lumen) from other internal tissues and organs.
The intestinal epithelium is composed of a single layer of cells and serves two crucial functions.
- It acts as a barrier, preventing the entry of harmful substances such as foreign antigens, toxins and microorganisms.
- It acts as a selective filter which allows the passage of dietary nutrients, electrolytes, water and various other beneficial substances from the intestinal lumen.
The gut barrier consists of 3 layers:
- Mucus layer, which prevents bacteria sticking to the surface
- Epithelial cells that allow water and nutrients to pass between layers
- Innermost layer with immune cells responsible for immune response against pathogens and harmful microbes
Disruption of the gut barrier can increase intestinal permeability, which increases the likelihood of unwanted material passing between the layers. For example, harmful microbes usually restricted to the intestinal lumen (the inside space of a tubular structure like the intestine) might pass into the bloodstream or trigger inappropriate immune responses and inflammation. This can lead to chronic disorders such as IBD.
The gut barrier can be strengthened through dietary fiber and probiotics. Fermentation of dietary fiber enhances the gut barrier seal and stimulates good bacterial growth, while probiotics can augment this further and help enhance body defenses.