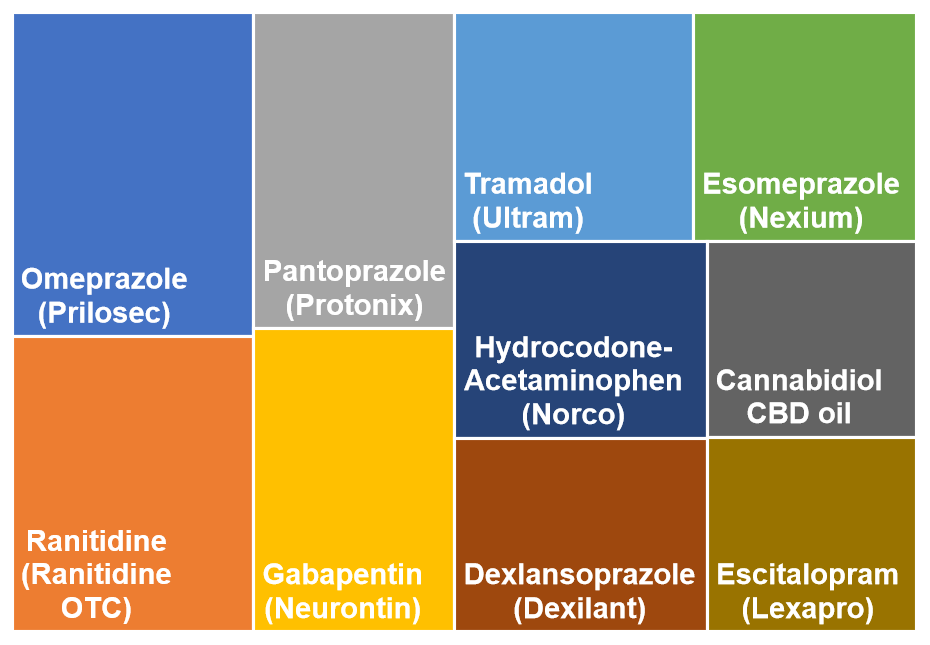
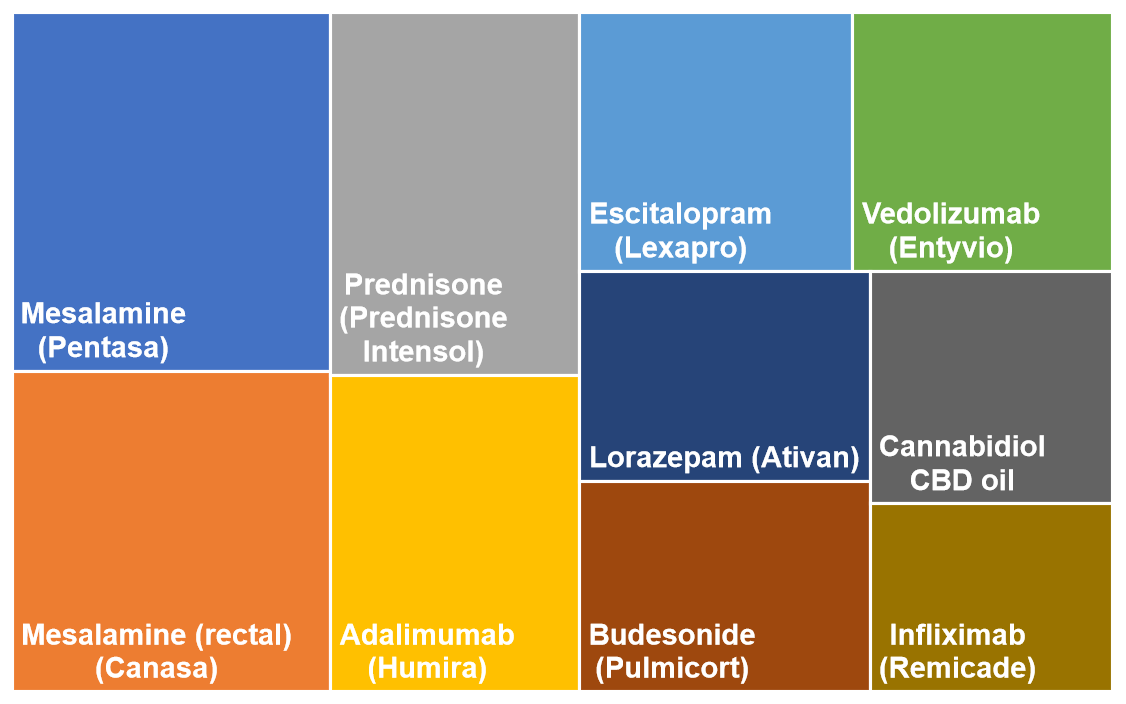
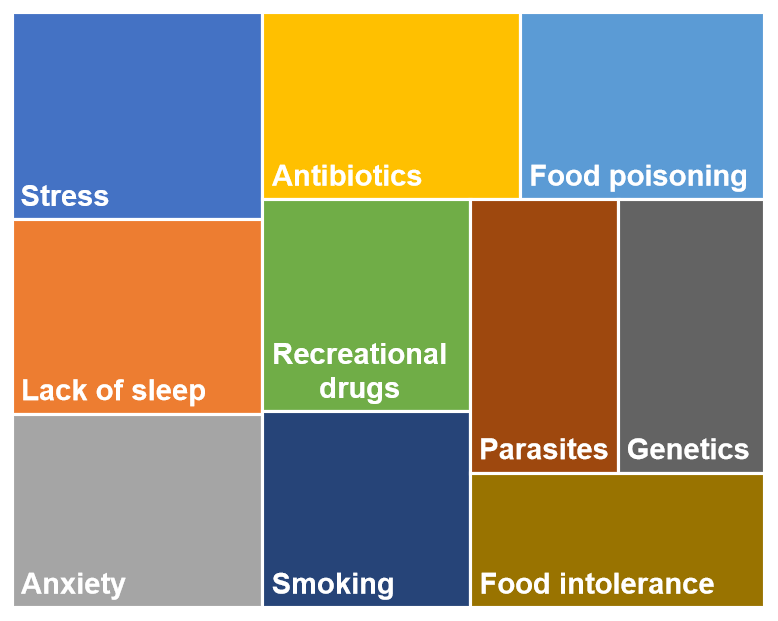
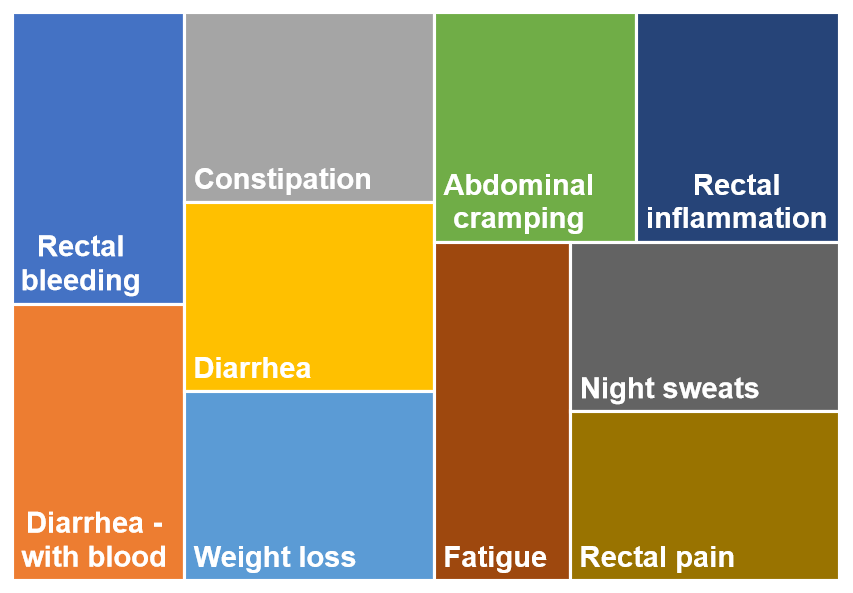
The chart below represents the top 10 symptoms for IBS. The box sizes in the chart represent the relative popularity based on votes.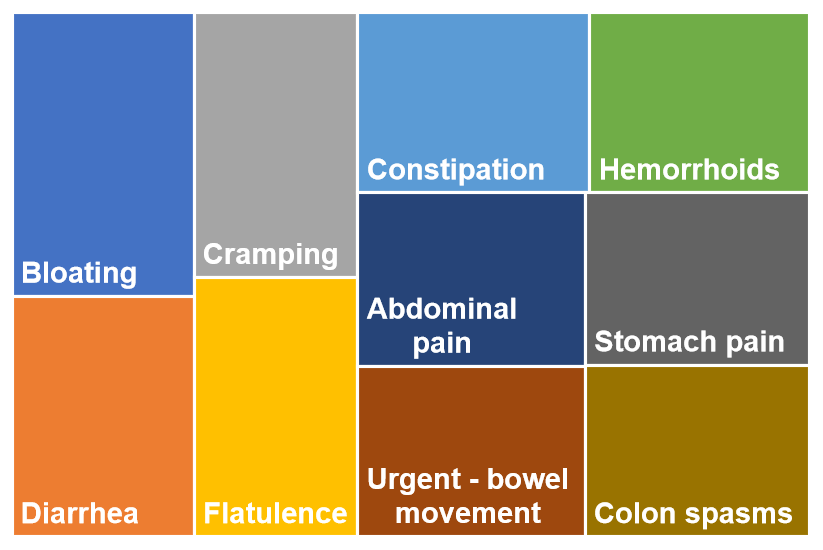
Decoding the Top Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is often described as a functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorder—meaning there is a problem with how the gut works, rather than a physical disease or structural damage. Despite the absence of visible inflammation or lesions, the symptoms experienced by individuals with IBS are intensely real, recurrent, and can profoundly disrupt their lives. Diagnosing IBS is typically a process of exclusion, relying heavily on a specific pattern of symptoms that have persisted over time, most notably the characteristic association of pain with changes in bowel movements. Understanding the full spectrum of these symptoms is essential, not only for diagnosis but for tailoring effective management strategies.
The accompanying chart visually highlights the Top Symptoms most frequently reported by those affected by IBS. While every individual’s experience is unique, the syndrome is fundamentally defined by a core cluster of complaints.
At the heart of the diagnostic criteria is Abdominal Pain or Discomfort. This cramping sensation is often the most debilitating and distressing symptom, typically located in the lower abdomen and a defining feature of the condition. Crucially, this pain is often related to, and frequently relieved by, passing a bowel movement. This relief distinguishes IBS pain from discomfort associated with many other GI conditions. The intensity and location of the pain can fluctuate, becoming worse during periods of stress or following the ingestion of certain trigger foods.
The second primary component involves Altered Bowel Habits, which is why IBS is subtyped into categories. Patients may primarily experience Constipation-Predominant IBS (IBS-C), characterized by infrequent, hard stools, difficulty passing movements, and a sense of incomplete evacuation. Conversely, others suffer from Diarrhea-Predominant IBS (IBS-D), marked by frequent, loose, and watery stools, often accompanied by a powerful and uncontrollable sense of urgency. Many individuals also contend with Mixed IBS (IBS-M), where they alternate between periods of both constipation and diarrhea.
Beyond these hallmark complaints, the GI system’s hypersensitivity often translates to a high prevalence of upper-GI symptoms. Bloating is one of the most common and bothersome issues, described as a feeling of uncomfortable fullness or pressure in the abdomen, which may be visibly noticeable (distention). This is frequently accompanied by excessive gas (flatulence). These symptoms are thought to be caused by irregular contractions of the intestinal muscles and a heightened sensitivity to gas accumulation, which would be unnoticed by a person without IBS. Other associated symptoms may include the presence of mucus in the stool, fatigue, and even challenges with the urinary system, underscoring that IBS is a complex disorder involving the entire gut-brain axis. Recognizing these top symptoms is the foundational step in seeking a diagnosis and working with a healthcare provider to craft a management plan that can minimize discomfort and restore a sense of predictability and control to daily life.
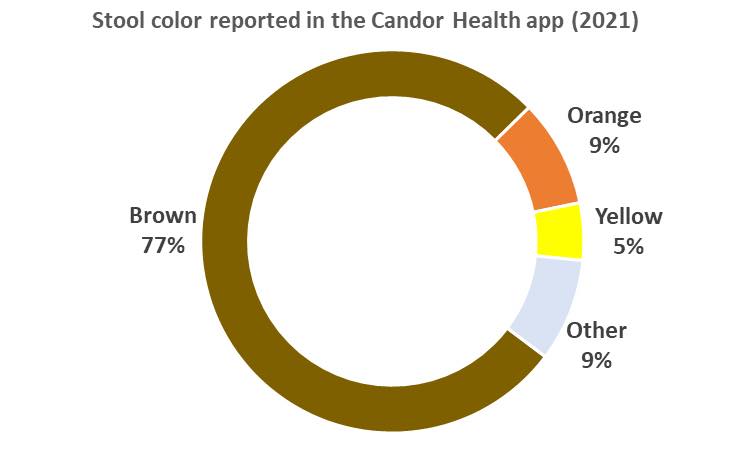
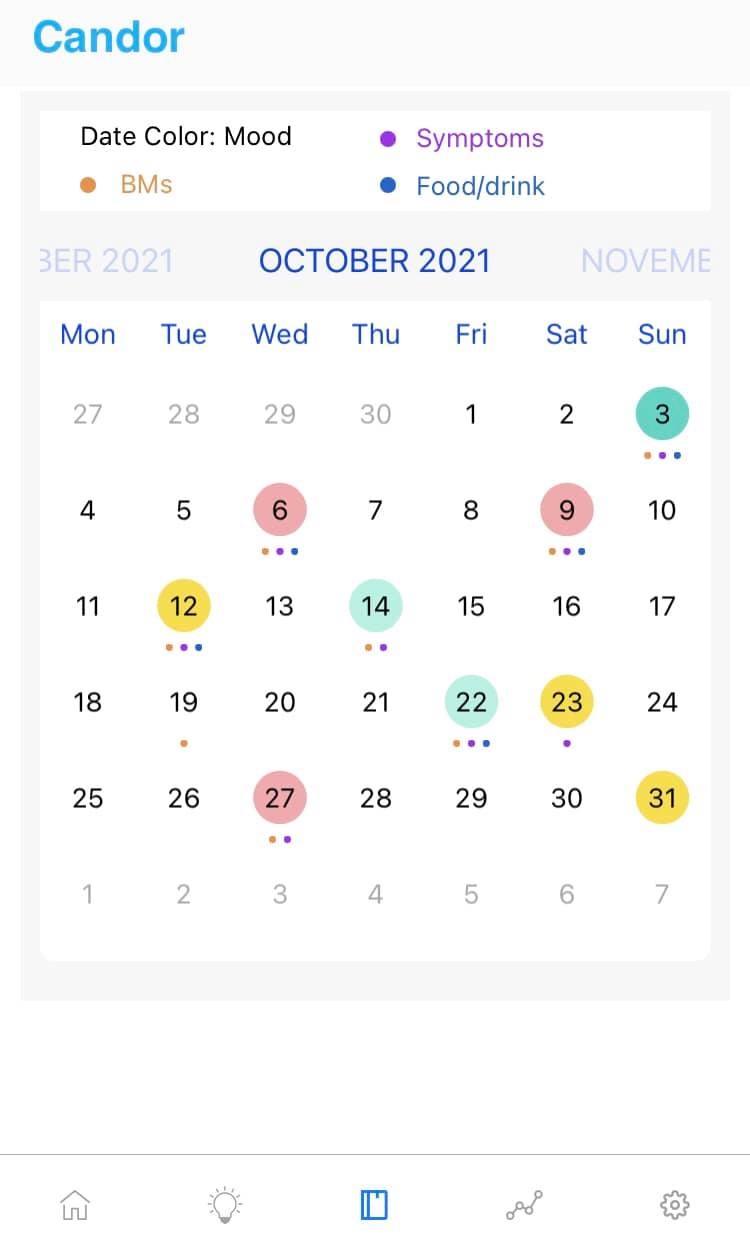
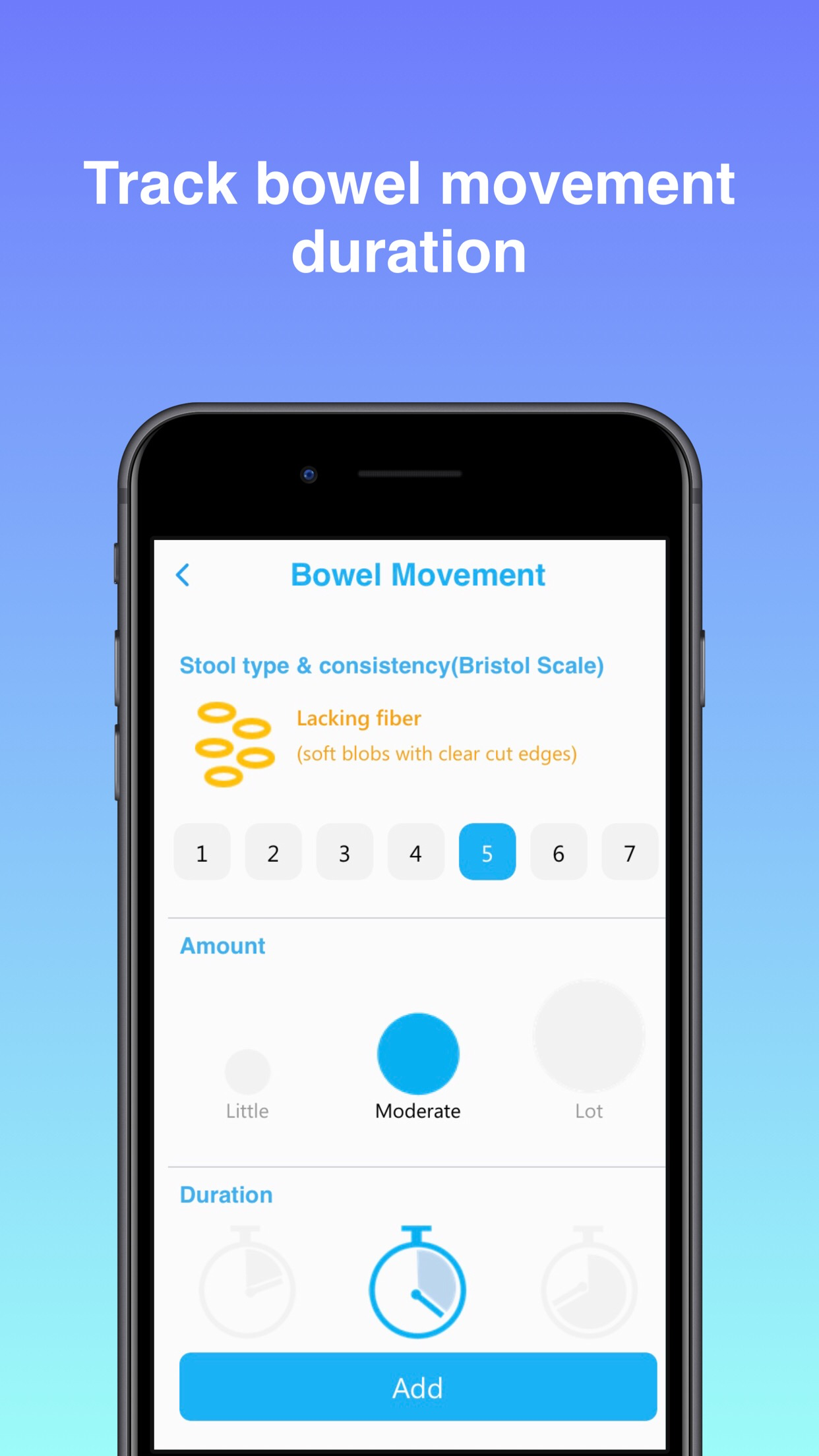
To see the full list, check out the Candor Health app.


The information presented in this article, including the discussion of the Top 10 IBS treatments, is intended solely for educational and informational purposes. It is designed to provide general knowledge and to promote a greater understanding of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and the various treatment approaches currently in use.
This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider, such as a physician or gastroenterologist, with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
- Do not use this information to self-diagnose or self-treat a health problem or disease.
- The effectiveness of any treatment can vary greatly from person to person.
- Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new diet, supplement, medication, or therapy.
Reliance on any information provided here is solely at your own risk.