Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common, chronic functional gastrointestinal (GI) disorder that significantly impacts the lives of millions worldwide. It’s characterized by recurrent abdominal pain or discomfort, associated with altered bowel habits—manifesting as diarrhea, constipation, or a mixed pattern. Unlike inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) such as Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis, IBS does not cause physical damage or inflammation visible upon examination, yet its symptoms are very real and can drastically reduce a person’s quality of life and productivity. The underlying cause is complex, involving dysfunction in the communication pathway between the gut and the brain—often referred to as the gut-brain axis—along with factors like visceral hypersensitivity (increased pain sensitivity in the gut), motility issues, and changes in the gut microbiome.
Because IBS presents differently in nearly every individual, successful management requires a highly personalized and holistic approach. There is no one-size-fits-all solution; instead, treatment focuses on relieving the most bothersome symptoms and restoring a greater sense of well-being. This necessarily involves a diverse array of therapeutic strategies that span the spectrum of modern healthcare, blending foundational lifestyle and dietary adjustments with targeted medical and psychological interventions. The aim is not just to control symptoms but also to address the various biological and psychological factors that contribute to the condition’s severity.
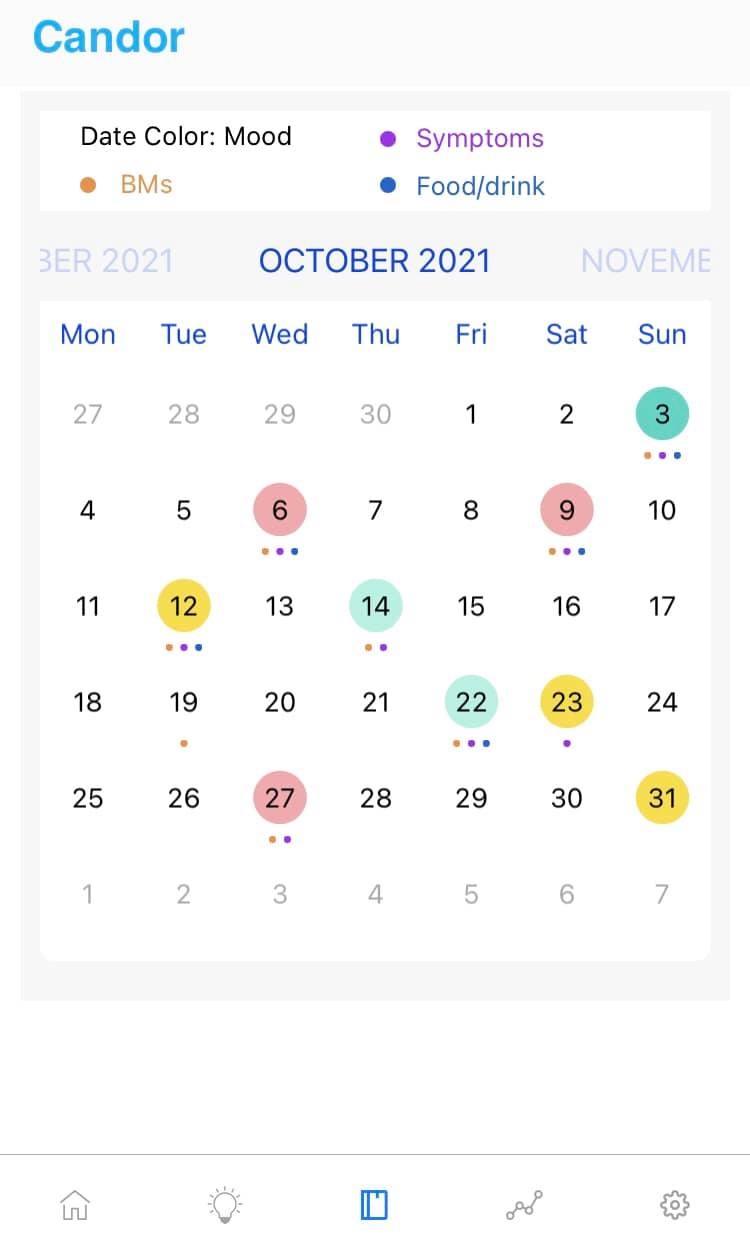
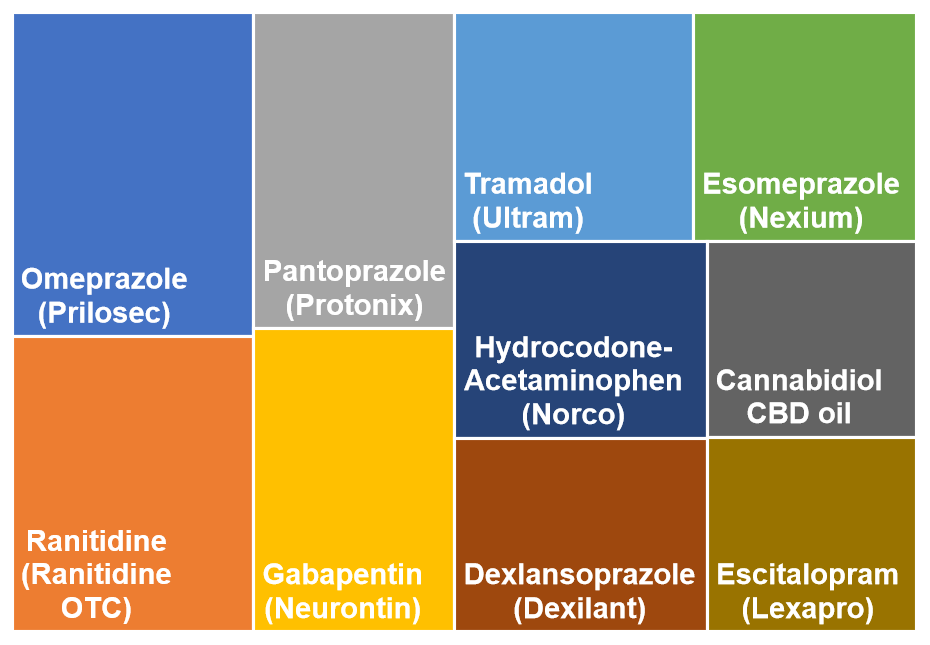
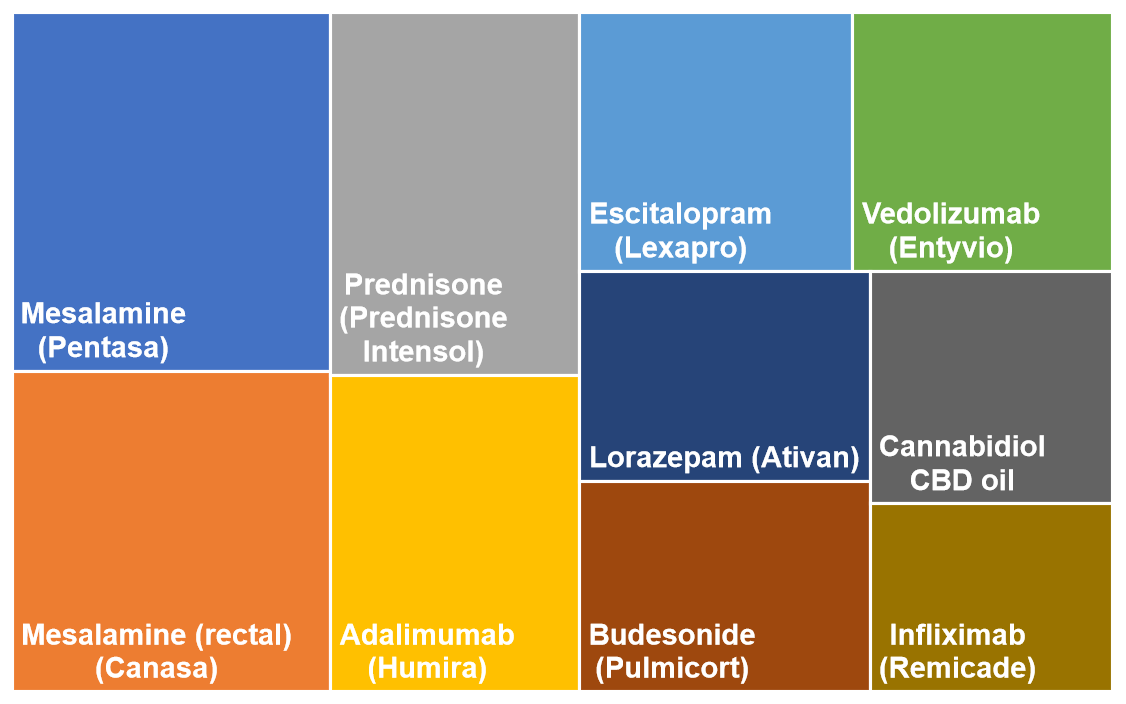
The accompanying chart presents a valuable overview of the Top 10 treatments currently being explored and utilized in the clinical management of IBS. This list is a reflection of the evolving understanding of this disorder, highlighting how effective management often requires a multi-pronged strategy. The treatments typically begin with non-pharmacological, low-risk interventions. For example, dietary modifications like the low FODMAP diet (which limits certain types of fermentable carbohydrates) are often recommended as a first-line approach due to their documented efficacy in reducing bloating, gas, and pain in many individuals. Similarly, addressing the mind-body connection through therapies such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) or Gut-Directed Hypnotherapy is increasingly recognized as a vital component, given the established role of stress and anxiety in modulating the gut-brain axis.
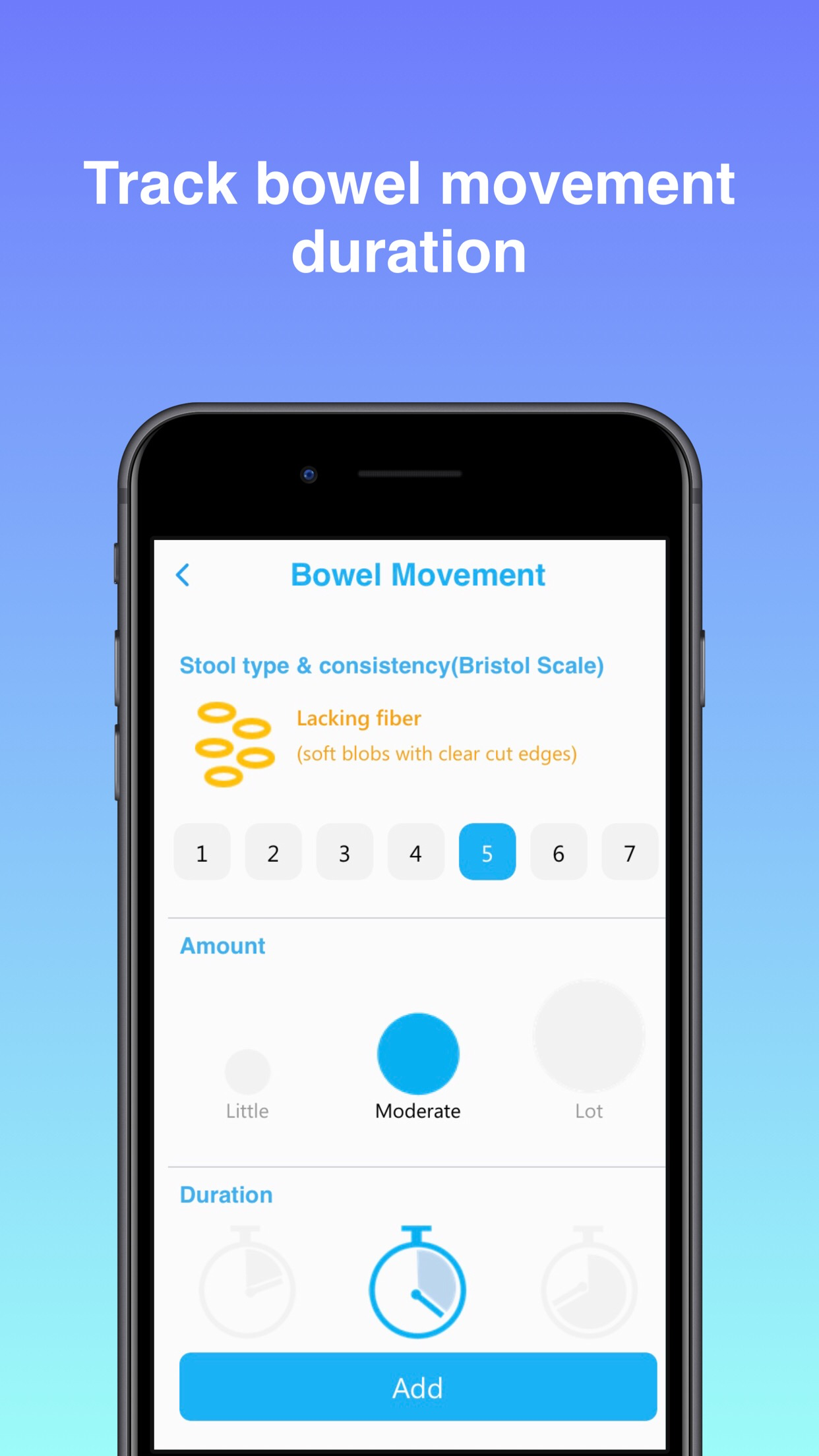
As the therapeutic journey progresses, individuals may integrate pharmacological options that are designed to target specific symptoms. These agents can include medications to manage chronic constipation, reduce urgent diarrhea, or alleviate abdominal spasms and pain. Furthermore, emerging evidence has focused attention on the gut microbiota, leading to the use of targeted probiotics or specific antibiotics to help balance the bacterial ecosystem within the gut. Ultimately, the treatments listed in this chart emphasize that effective IBS management is a collaborative effort between the patient and their healthcare provider, requiring patience and a willingness to explore different options to find the optimal combination that brings sustained relief.
To see the full list, check out the Candor Health app.


The information presented in this article, including the discussion of the Top 10 IBS treatments, is intended solely for educational and informational purposes. It is designed to provide general knowledge and to promote a greater understanding of Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) and the various treatment approaches currently in use.
This content is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.
Always seek the advice of a qualified healthcare provider, such as a physician or gastroenterologist, with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read in this article.
- Do not use this information to self-diagnose or self-treat a health problem or disease.
- The effectiveness of any treatment can vary greatly from person to person.
- Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new diet, supplement, medication, or therapy.
Reliance on any information provided here is solely at your own risk.