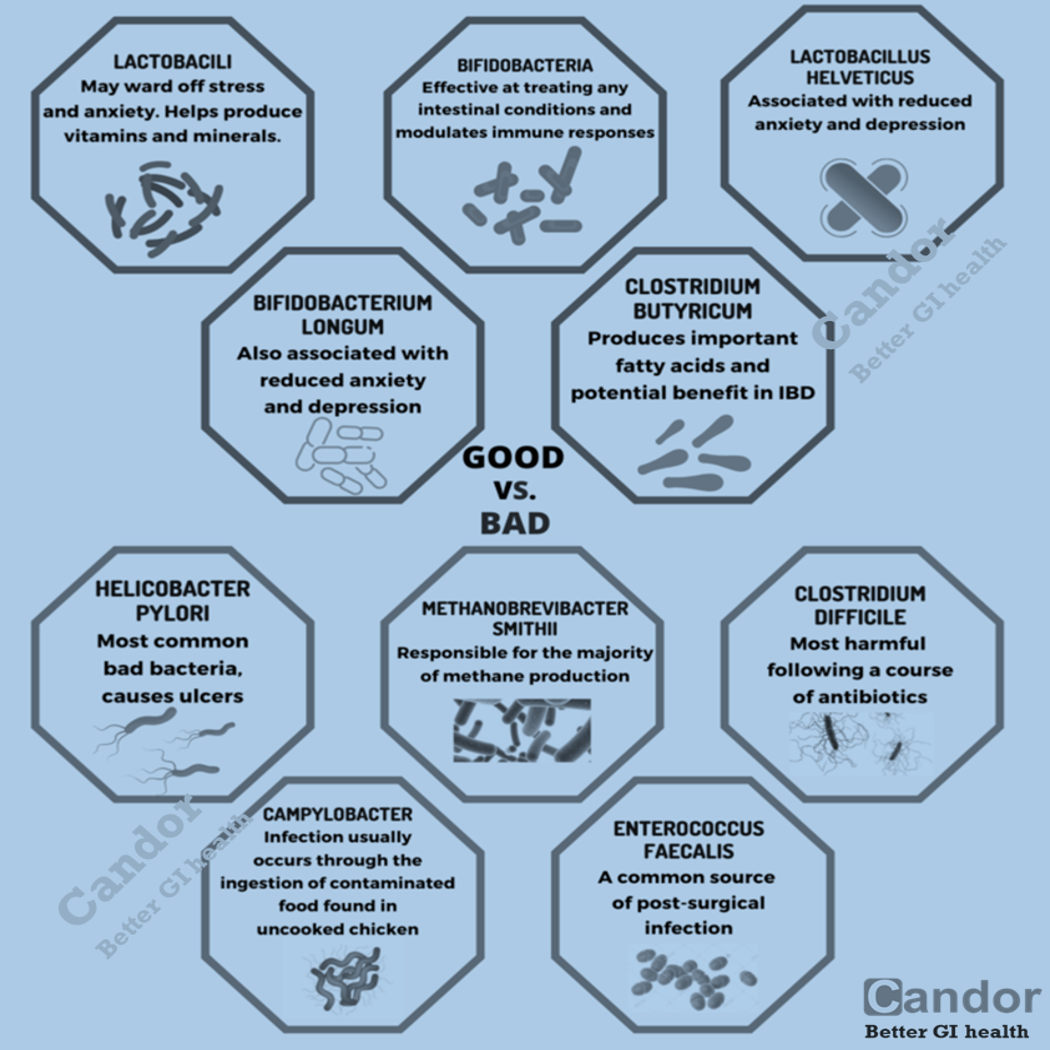
Different Colors of Stool
While brown is considered the “normal” color s for stool, greenish-brown hues may also be seen as normal.
Some other colors are:
- Black: Stools that are black, especially if they have the appearance of coffee grounds, suggest GI bleeding. Iron supplements, black licorice, black stout, and bismuth medications also cause black stool.
- White: Stools that are white, gray, or pale may be caused by an issue with the liver or gallbladder. The pale color is due to the lack of bile. Some anti-diarrhea medications can also cause white stools.
- Green: Spinach, kale, or other green foods can cause green color in stool. However, green-colored stool may be a sign that there is too much bile and not enough bilirubin in the stool.
- Red: Redness in stool may be the result of gastrointestinal bleeding. While small amounts of blood in the stool can indicate hemorrhoids, eating beets, red berries or tomato juice can also turn stool red.
- Orange: Consuming foods rich in a pigment called beta-carotene can cause orange stool. Carrots, sweet potatoes, and winter squash are among the many foods that contain this pigment. Other causes could be blocked bile ducts or certain medications including some antacids and some antibiotics.
- Yellow: Yellow or greasy-looking stool suggests excess fat and may be the result of absorption issues, or difficulty producing enzymes or bile.
Variations in stool color is common and usually down to diet or some other minor cause. However, changes in stool color that last for 2 or more weeks, especially red or black stool warrant a visit to the doctor.

Are you interested in finding out more about your gut health? Follow our social media accounts to be updated on all of our informative content.
And if you want to be a part of our amazing community on Facebook, you can join by clicking here.
Like us on Facebook and Follow us on Instagram
#gutproblems #gutissues #bloatingproblems #sibo#sibodiet#ibs#ibsdiet#eliminationdiet #foodintolerances#foodsensitivities#foodallergies#guthelp#healyourguthealyourlife