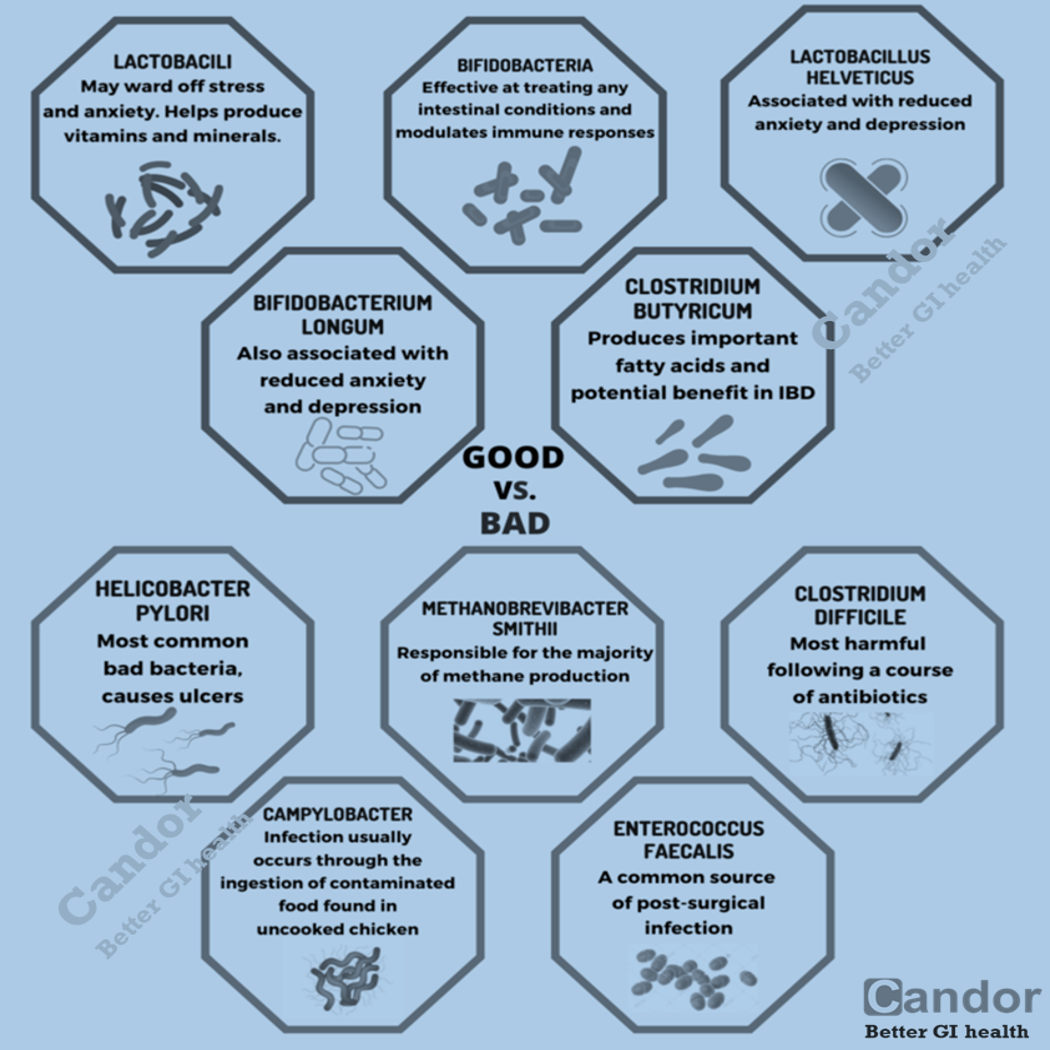
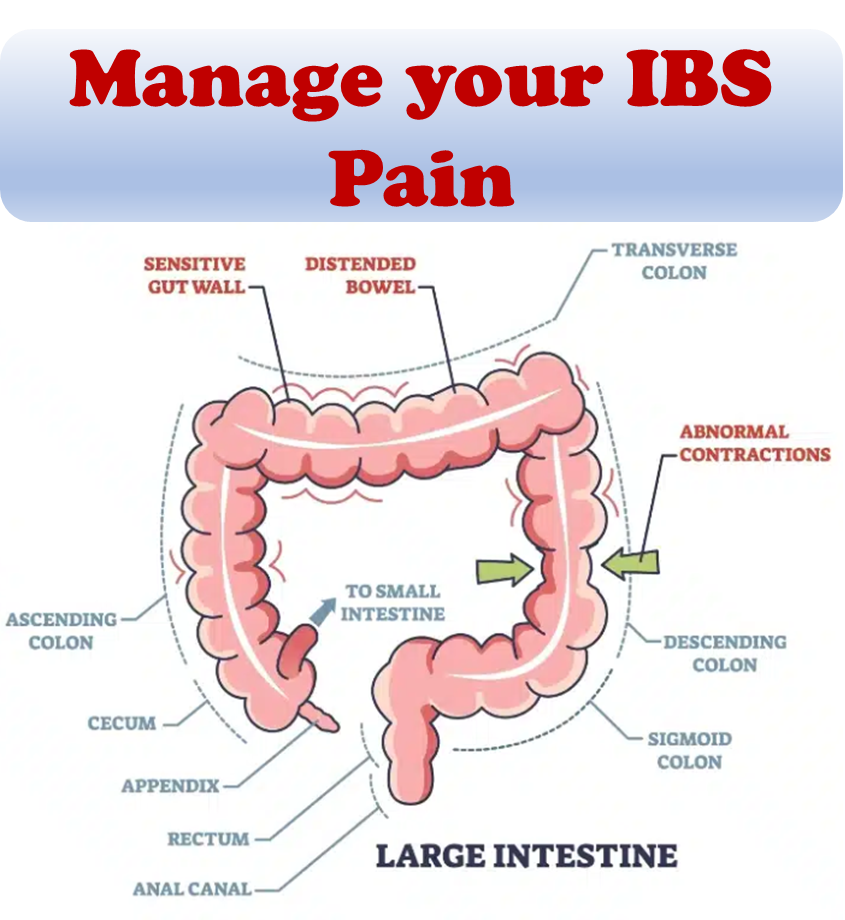
The exact cause of IBS is unknown. IBS is a diagnosis of exclusion, which means that other diseases and infections must be ruled out before it can be diagnosed. Physicians often run several tests to ensure that there is no inflammation, infection, or other disease causing the symptoms. Diagnosing IBS typically involves a physical exam and medical history.
Since it is important to exclude other GI conditions, doctors don’t use tests alone to diagnose IBS. The evaluation may include blood tests, stool samples, endoscopic procedures (such as sigmoidoscopy and colonoscopy), or imaging procedures (like a CT scan or MRI). In patients with IBS, anemia is not apparent, stool calprotectin is normal, and no inflammation is seen on endoscopy or imaging tests.
Blood test: A health care professional will take a blood sample from you and send the sample to a lab. Doctors use blood tests to check for conditions other than IBS, including anemia, infection, and digestive diseases.
Stool test: The doctor will give the patient a container for catching and holding a stool sample, with instructions on where to send or take the kit for testing. Doctors use stool tests to check for blood in your stool or other signs of infections or diseases. The doctor may also check for blood in the stool by examining your rectum during your physical exam.
Other tests: Doctors may perform other tests to rule out health problems that cause symptoms similar to IBS symptoms. The doctor will decide whether other tests are needed based on:
- blood or stool test results
- family history of digestive diseases, such as celiac disease, colon cancer, or inflammatory bowel disease
- symptoms that could be signs of another condition or disease
There could also be other tests to get to a definitive assessment:
- hydrogen breath test to check for small intestinal bacterial overgrowth or problems digesting certain carbohydrates, such as lactose intolerance
- upper GI endoscopy with a biopsy to check for celiac disease
- colonoscopy to check for conditions such as colon cancer or inflammatory bowel disease
Follow us on:
http://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp