Fermented foods are defined as foods or beverages produced through controlled microbial growth, and the conversion of food components through enzymatic action. In recent years, the benefits of fermented foods have created a surge in popularity, mainly due to their proposed health impacts. There are several mechanisms through which fermented foods may exert beneficial effects in health and disease.
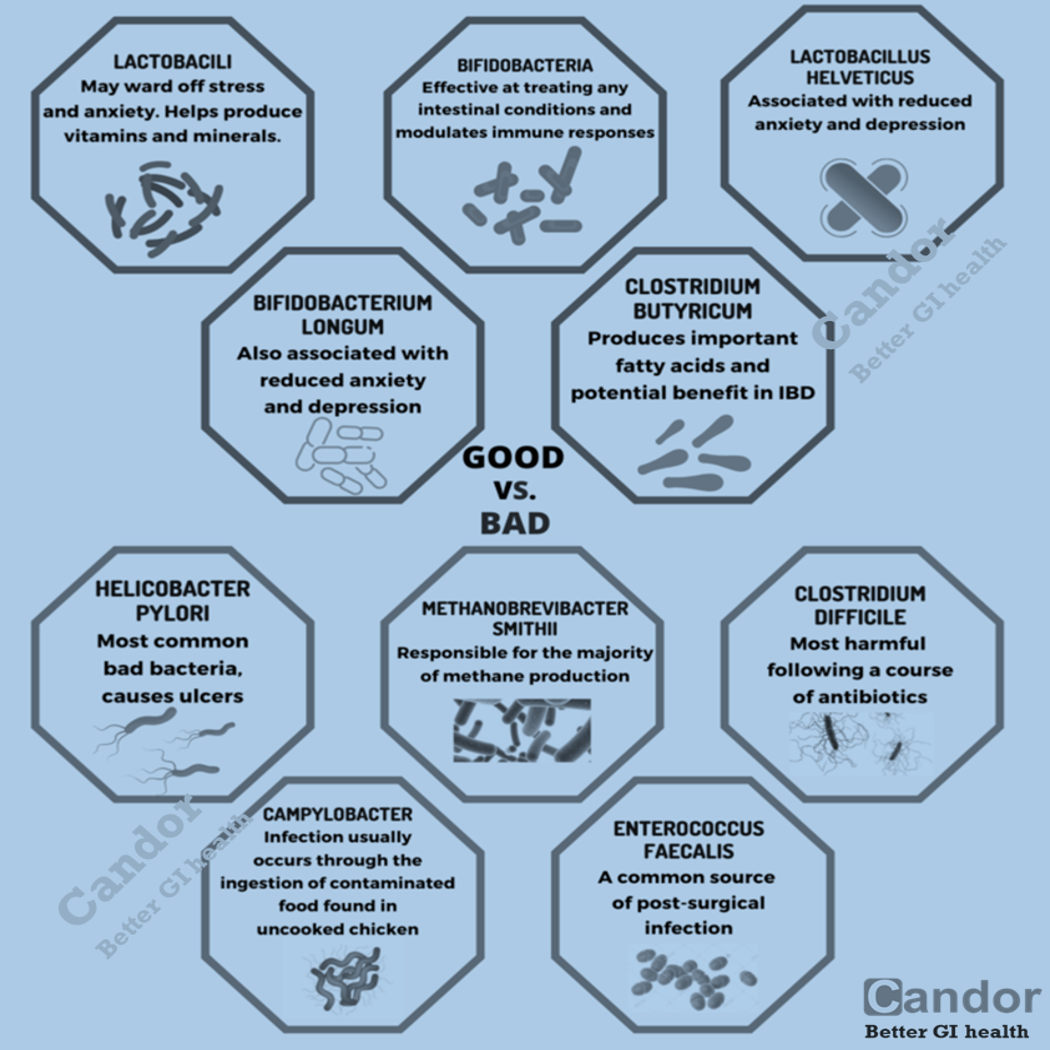
- They contain potentially probiotic microorganisms, such as lactic acid bacteria.
- Fermentation-derived metabolites may exert health benefits. For example, lactic acid bacteria (relevant to both dairy and non-dairy fermented foods) generate bioactive peptides and polyamines with potential effects on cardiovascular, immune and metabolic health.
- Fermentation may convert certain compounds to biologically active metabolites and food components found in fermented foods, such as prebiotics and vitamins, may also exert health benefits.
- Fermentation can reduce toxins and anti-nutrients. For example, sourdough fermentation can reduce the content of fermentable carbohydrates (e.g., fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides and polyols, FODMAPs), which may increase the tolerance of these products in patients with functional bowel disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
Follow us on: http://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp