The recommendations for management of IBS should include information that explains the importance of self‑help in effectively managing IBS symptoms. This should include information on general lifestyle, physical activity, diet and symptom‑targeted medication. Here are some of the common recommendations for management for IBS:
- People with sedentary lifestyles are usually encouraged to increase their physical activities
- Medical professionals encourage people with IBS to identify and make the most of their available leisure time and to create relaxation time
- Eat regular meals and avoid rushing at mealtime. Avoid missing meals or leaving long gaps between meals.
- Drink at least 8 cups of water daily, and restrict tea and coffee to 3 cups per day.
- Reduce intake of alcohol and carbonated drinks.
- Limit intake of high‑fiber foods and reduce ‘resistant starch’ which is often found in processed or re‑cooked foods (resistant starch resists digestion in the small intestine and reaches the colon intact).
- IBS-D can be exacerbated with sorbitol, an artificial sweetener found in sugar‑free sweets and drinks.
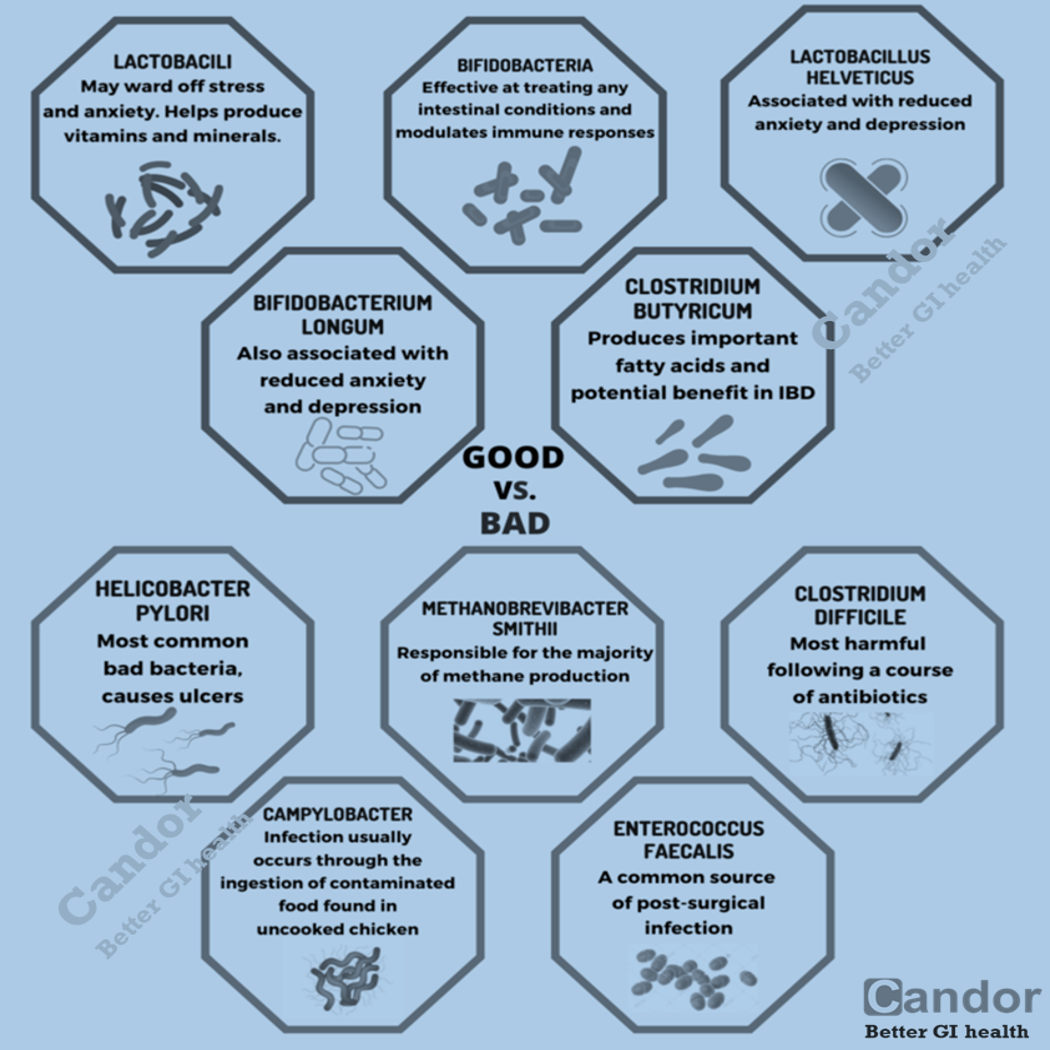
- Introduce probiotics for at least 4 weeks while monitoring the effect. Probiotics should be taken at the dose recommended by the manufacturer.
- Single food avoidance and exclusion diets (for example, a low FODMAP) should only be advised on and monitored by a healthcare professional with expertise in dietary management.
Follow us on: https://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp