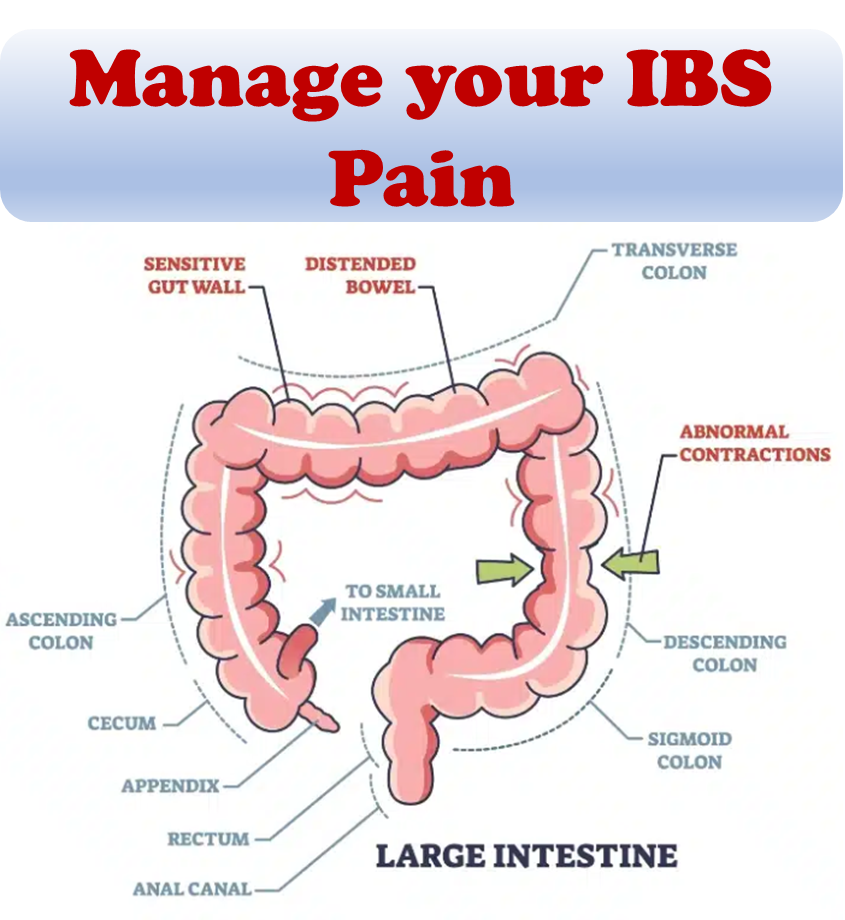
IBS does not have a cure, and does not go away with medication or special diets. The primary preventative measure is to identify and avoid individual triggers. Some treatment options that have been explored include one or more of the following:
Diet:
- A modest increase in dietary fiber, with plenty of clear fluids
- Reducing or eliminating common gas-producing foods, such as beans and cabbage
- Reducing fatty foods, sweeteners, caffeine and alcohol
- Reducing or eliminating dairy foods, if lactose intolerance is a trigger
- Establishing eating habits or routines and avoiding sudden changes to habits
- A low-FODMAP diet can be explored as a solution. This diet should be commenced with the supervision of a dietician experienced in administering the diet and familiar with IBS. The diet involves eliminating these carbohydrates from your diet for a period of six to eight weeks and then gradually adding them back into your diet to assess for tolerance
Medications:
- Anti-diarrhea medication – these can be an essential part of management in those with IBS-D (diarrhea-predominant)
- Pain-relieving medication – opiates such as codeine can provide effective pain relief. One of their most common side effects, constipation, may also relieve the diarrhea of IBS-D
- OTC treatments for constipation
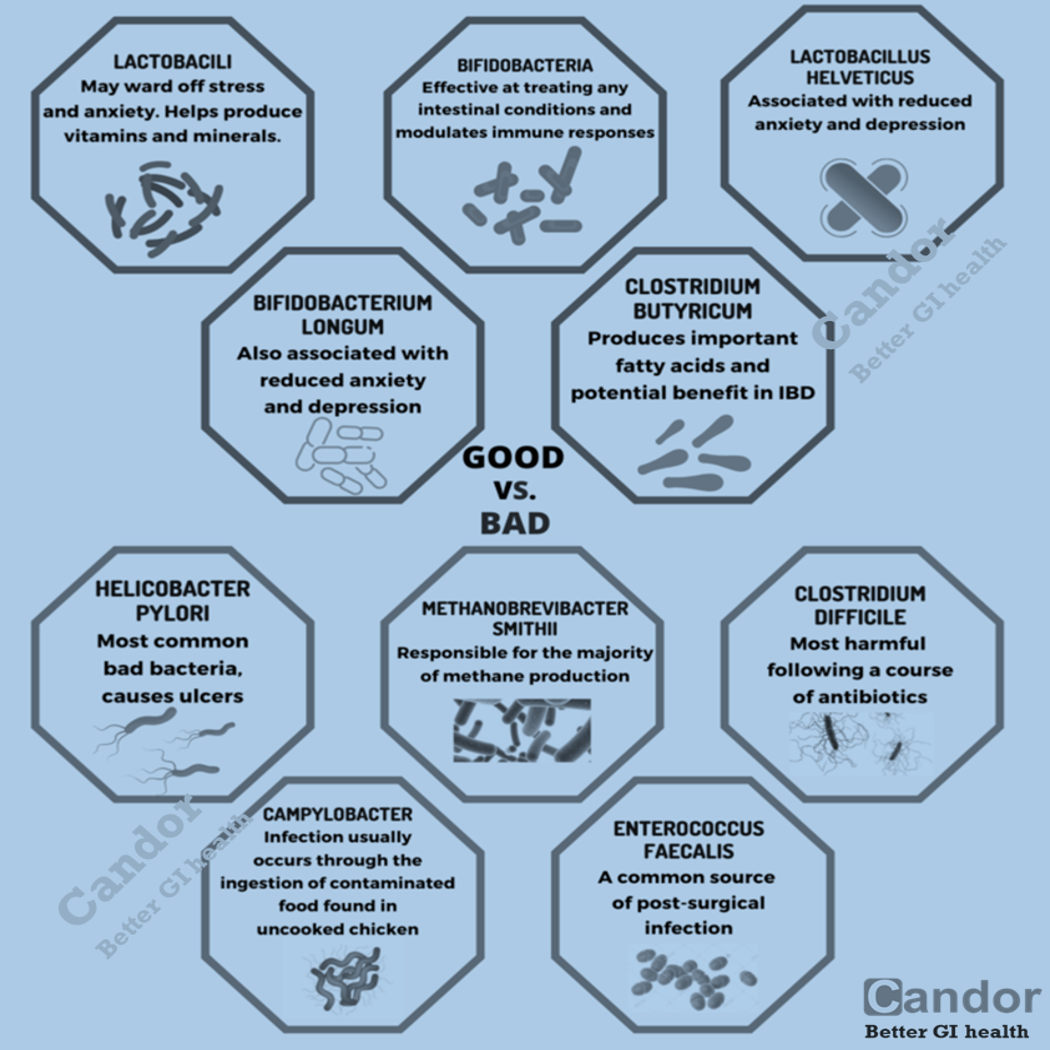
- Probiotic supplements that contain live strains
- Anti-spasmodic drugs, which may ease cramping. Antispasmodics work best if taken 30 to 60 minutes prior to eating and may be better at providing short-term relief of symptoms
- Pharma companies have been working to develop IBS specific medications, which typically work on receptors within the large intestine to bring about IBS symptom relief
- Some studies have indicated that peppermint oil has strong antispasmodic qualities, and may work for some people in easing IBS pain
- Tricyclic anti-depressants can be effective in treating the pain of IBS, but are best prescribed for a trial period with active monitoring of symptoms. Doctors are more likely to recommend an antidepressant if symptoms have not been addressed through lifestyle and dietary changes
Lifestyle and behavioral therapies:
- Stress management, especially if stress Is a regular trigger for flare-ups
- Regular physical activity in whatever form has been effective for some. It may be worthwhile to experiment with a few routines to find what works best (yoga or running, for example)
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and gut-directed hypnotherapy have the most research support for their effectiveness in reducing IBS symptoms. CBT focuses on challenging and changing unhelpful thoughts, beliefs and behaviors, improving emotional regulation, and the development of personal coping strategies that target solving current problems.
Follow us on:
http://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp