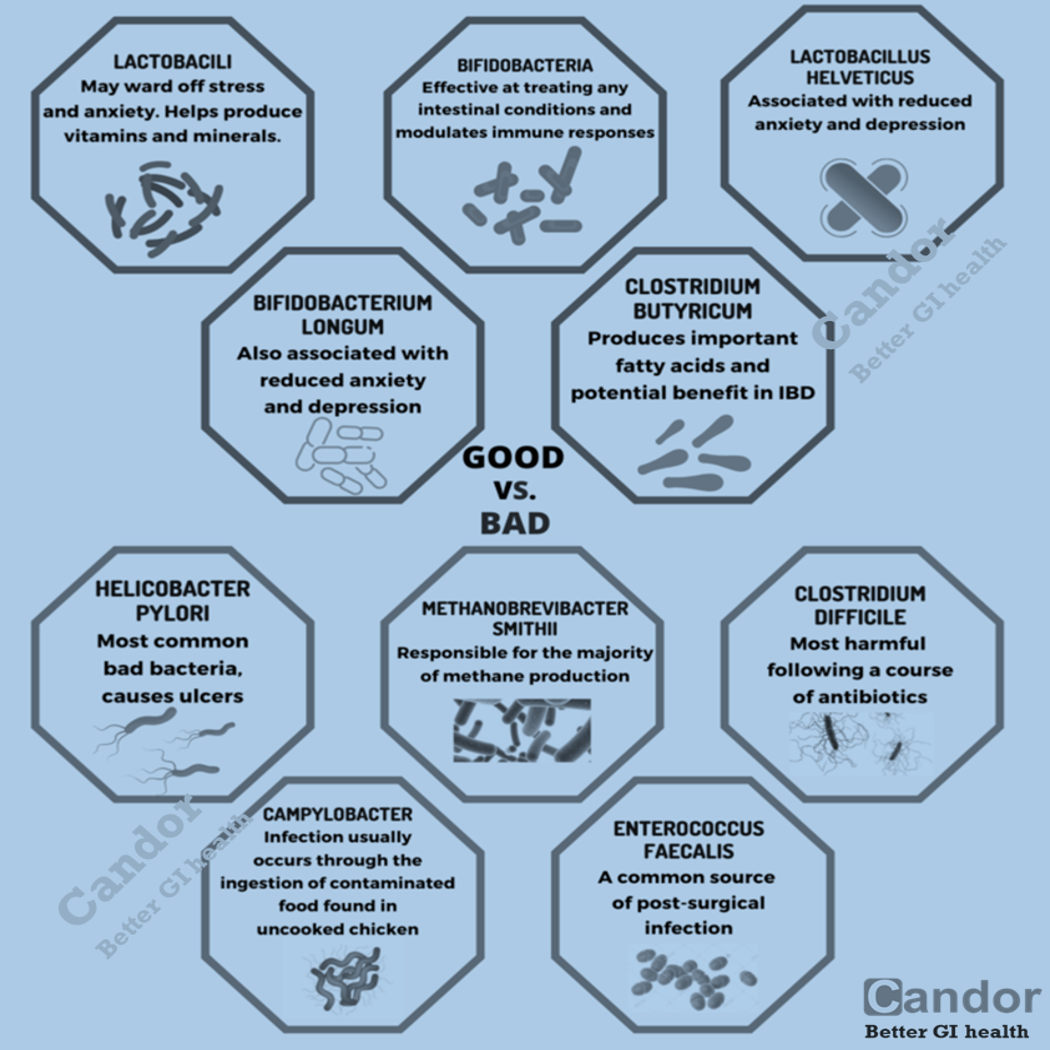
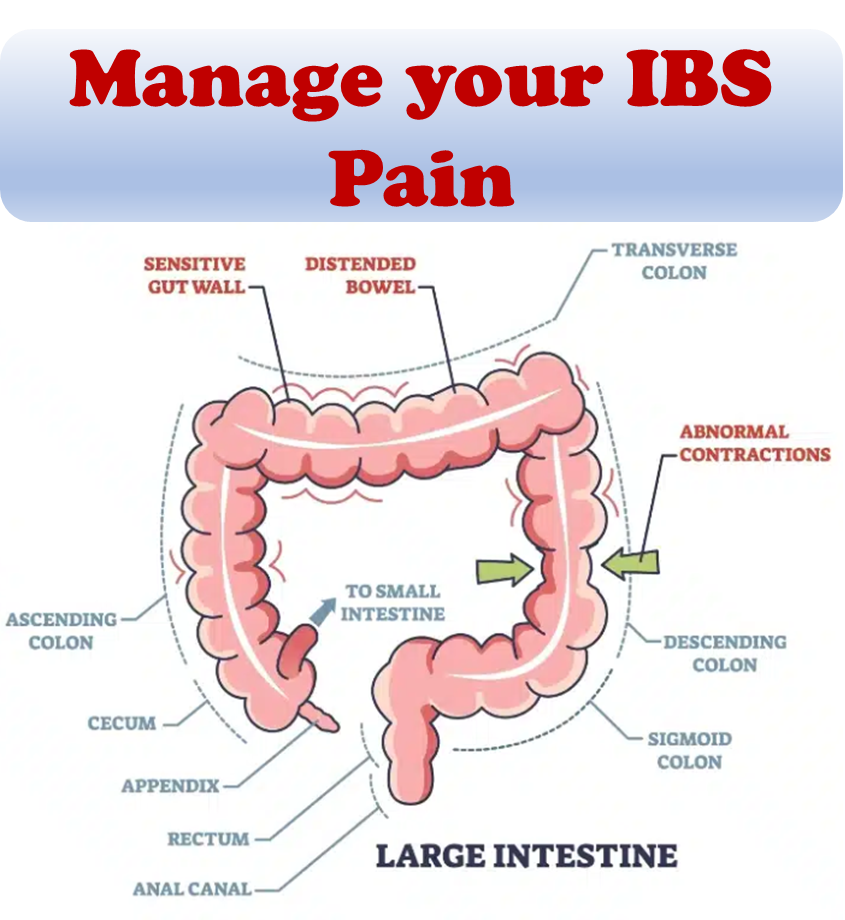
The microbiota refers to the collective community of microbes, that live on or within different parts of our bodies, like the skin, mouth, and gut. The gut microbiota is made up of trillions of bacteria and other microbes that play important roles in helping maintain our health. A healthy gut microbiota helps with digestion, keeps our immune system in fighting shape, and protects us from harmful microbes. An imbalance or a loss of diversity in the microbiota can cause a number of symptoms. For example, antibiotics tend to affect this balance, and cause issues such as diarrhea.
Microbial metabolites are produced by gut microbes during fermentation of food components that the intestine cannot process or absorb. There are hundreds of thousands of metabolites produced in the gut, and it is estimated that up to 40% of the metabolites measurable in our blood originate from the gut microbiota.
Diet has an effect on an individual’s gut microbes. The metabolites produced by microbes varies based on what they are fed. These metabolites may have an effect on the nervous system both in the gut (the enteric nervous system) and in the brain. Our diet can have either a positive or a negative effect on our gut microbiota.
The low FODMAP diet reduces consumption of certain dietary fibers that support beneficial microbes in our gut. Short term, the diet may alleviate symptoms for some IBS patients since there is less gas produced by gut bacteria from digestion, but long term the diet can be difficult to maintain, and can potentially have negative effects on gut microbiota and their diversity. Looking ahead for people with functional GI disorders like IBS, it will be important to find the optimal diet for each individual. There is new evidence, which suggests that the benefits to a particular diet depend on the individual gut microbial composition of the person.
Stress is also a factor, as feeling anxious or angry or sad while eating affects gut functions like contractions and secretion. Stress can also affect the microbiota if the stress or emotional distress is chronic. A balanced mind and an individualized diet may be the key to maximizing benefits for GI and overall health.
:
http://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp
Source: The 2016 Gut Microbiota for Health World Summit, organized by the American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) and the European Society of Neurogastroenterology & Motility (ESNM)