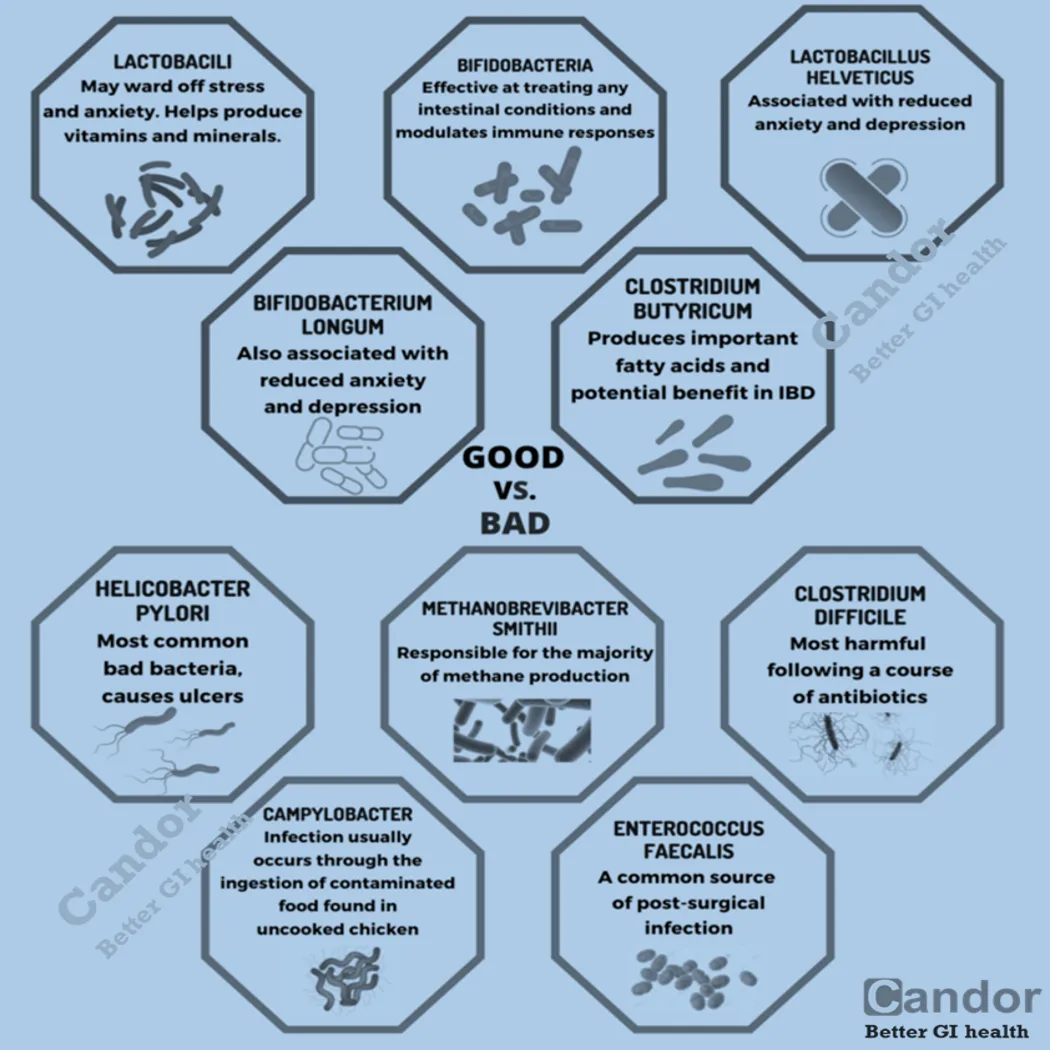
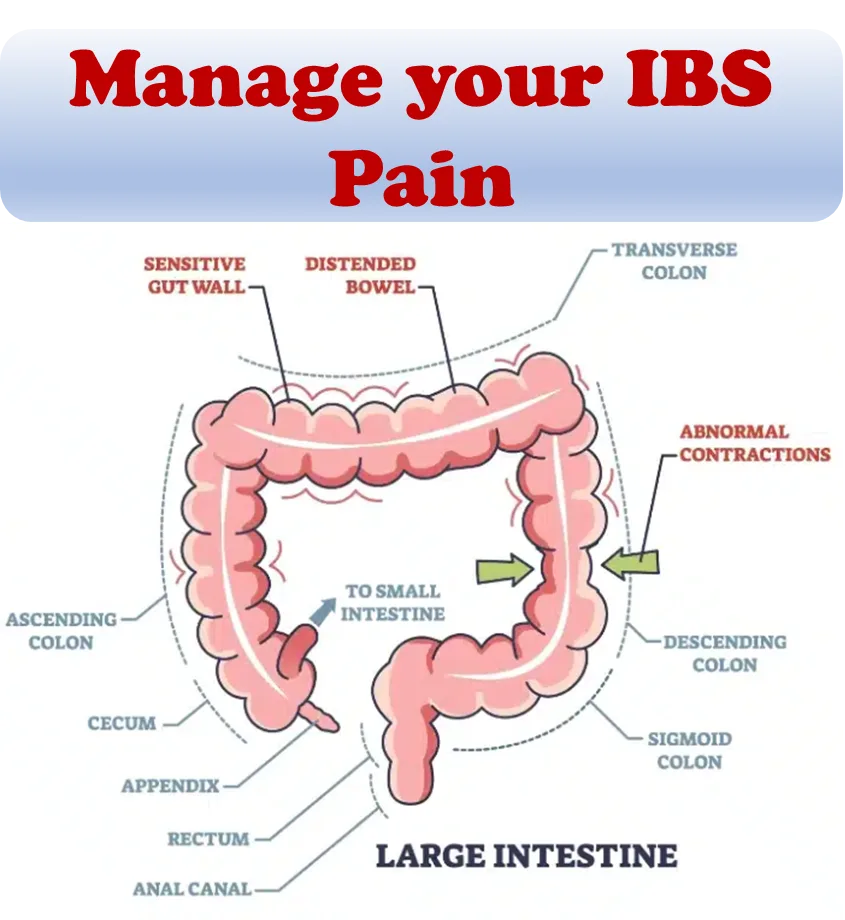
A major scientific breakthrough in understanding the interaction of the nervous system with the digestive system occurred with the discovery of the so-called enteric nervous system (ENS) in the middle of the 19th century. The ENS is a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is often called the “second brain”.
- In humans, the enteric nervous system in about 500 million neurons (0.5% of the number of neurons in the brain)
- This is about five times the number of neurons in our spinal cord
- The ENS is embedded in the lining of the gastrointestinal system, beginning in the esophagus and extending down to the anus
- The ENS is capable of operating independently of the brain and spinal cord
- The neurons of the ENS control the motor functions of the system, in addition to the secretion of gastrointestinal enzymes. Through intestinal muscles, the motor neurons control peristalsis and churning of intestinal contents while other neurons control the secretion of enzymes
- The ENS has the capacity to alter its response depending on such factors as bulk and nutrient composition
- More than 90% of the body’s serotonin lies in the gut, as well as about 50% of the body’s dopamine, which is currently being studied to further our understanding of its utility in the brain
- While the ENS has long been known to control digestion, researchers are analyzing its role in our physical and mental well-being
Follow us on:
http://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp