8 Common FODMAP Beliefs and Insights
“I’ve been experiencing diarrhea, bloating and abdominal pain for several months now – I must have IBS and should try a low FODMAP diet.”
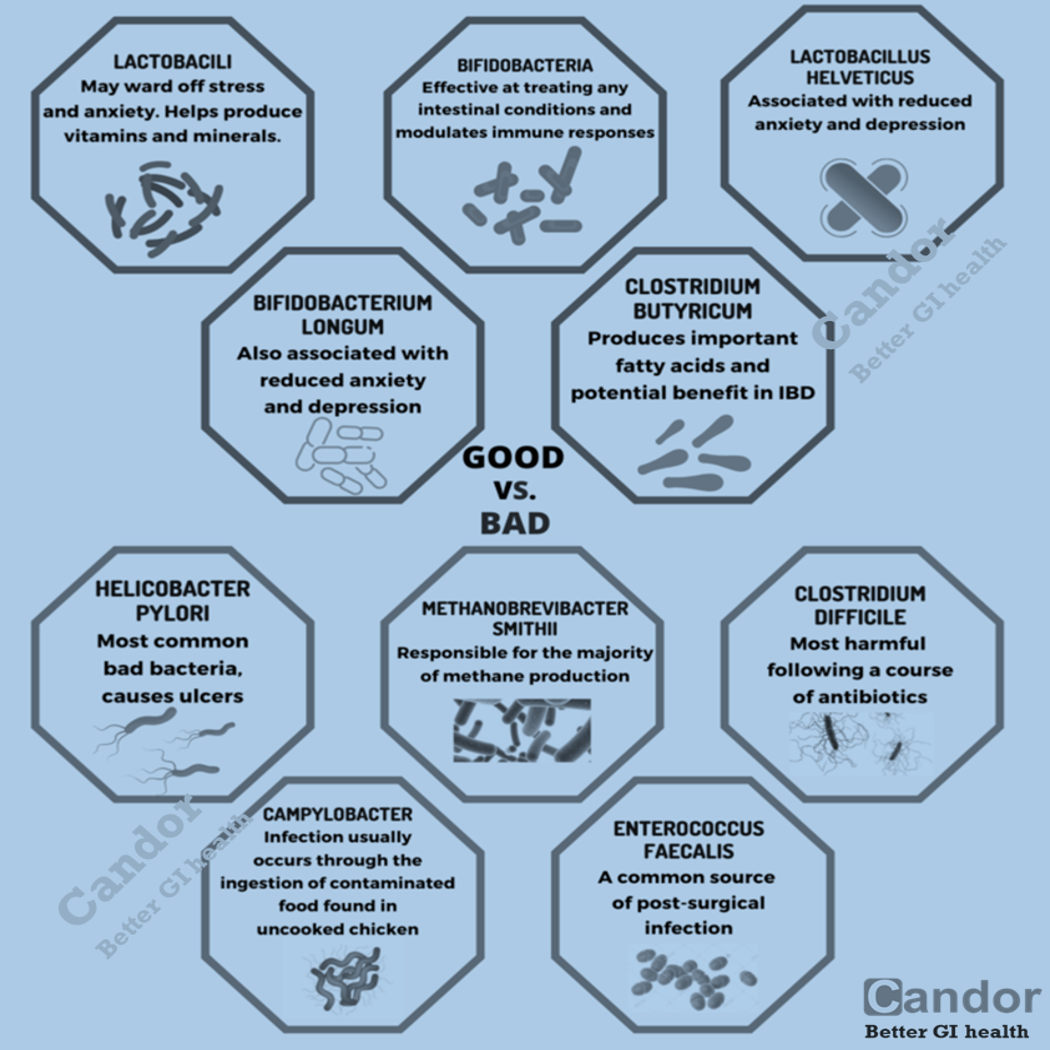
It’s important to consult your physician for a correct diagnosis before attempting any diets. Gut symptoms including diarrhea, bloating and abdominal pain can occur for many reasons, and may indicate that you have a medical condition other than IBS.
This is because chronic conditions such as celiac disease and IBS can also present with similar symptoms.
“Following a low FODMAP diet will cure my IBS.”
The low FODMAP diet is not a cure for IBS. Instead, it is used produce symptom improvement and studies have shown that long-term symptom benefits/control is maintained for people following a personalized FODMAP diet.
“I should be strictly avoiding FODMAPs when following a low FODMAP diet.”
There’s no one approach for everyone – it depends on you and your needs.
A health care professional and dietician can help determine how strictly you need to follow the diet, or whether a more simplified approach is best.
“Low FODMAP diet is gluten free.”
No – many gluten-containing grains (e.g. barley, rye, wheat) are present in a reduced quantity on a low FODMAP diet.
Gluten-free products tend to have a lower fiber content and this may compromise your fiber intake on the diet.
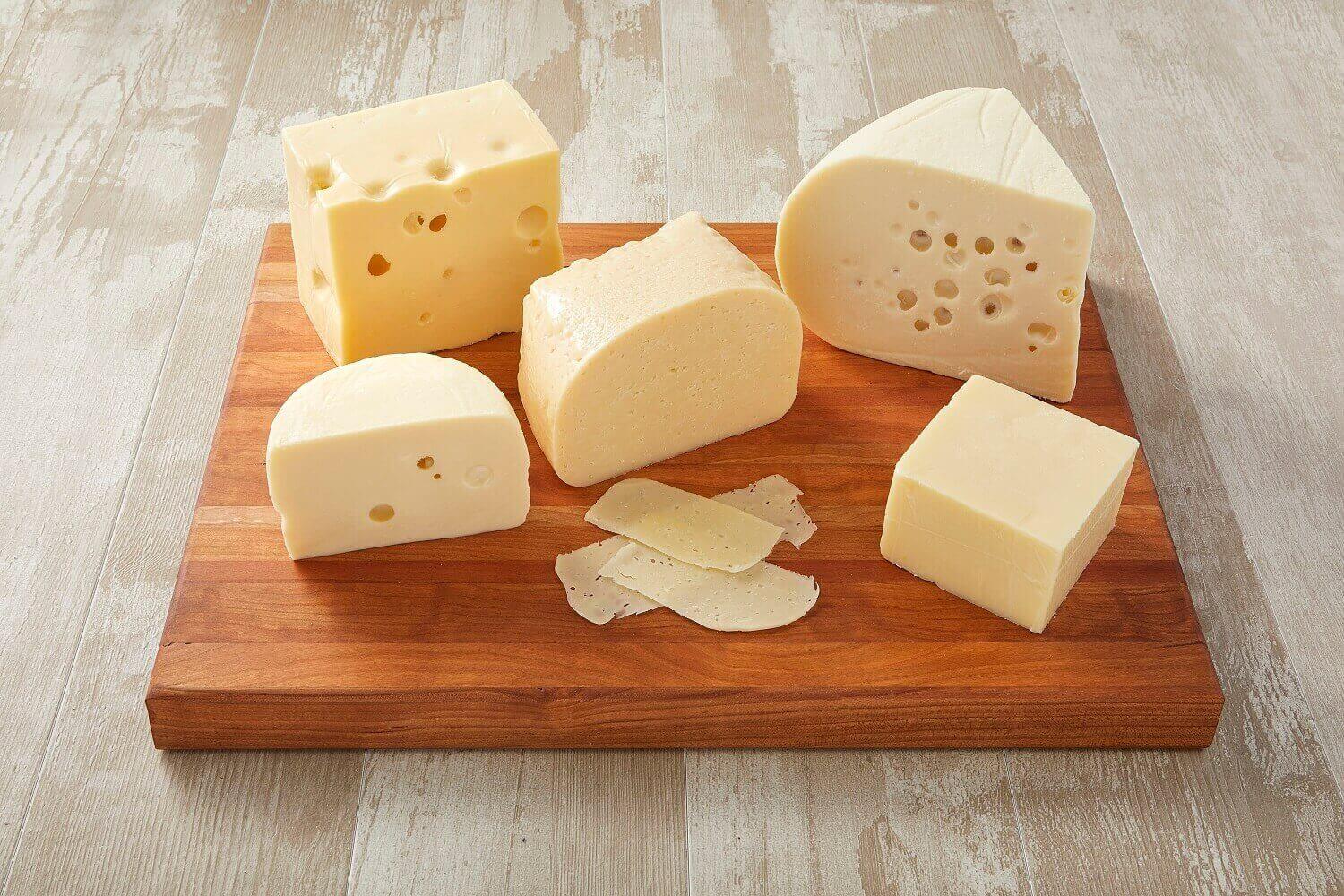
“The low FODMAP diet is dairy-free.”
No, the low FODMAP diet is not a dairy-free diet. Lactose is the major FODMAP present in some dairy products. Reducing lactose intake can be achieved by adding lactose-free alternatives or calcium-fortified, low FODMAP suitable plant milks into the diet.
A range of mature or ripened cheese (cheddar, Swiss, fetta, brie) also contain very little lactose content.
“Low FODMAP diet is low on protein.”
Protein-rich sources such as meat, fish, eggs and poultry are low in FODMAP.
Vegetarian diets can include tempeh, firm tofu, chickpeas, lentils and higher protein grains such as buckwheat and quinoa.
“A low FODMAP diet is a long-term process.”
A low FODMAP diet is typically followed for about 2-6 weeks to ensure sufficient symptom relief, followed by a reintroduction period and personalization.
The reintroduction phase can be started earlier if your symptoms have resolved before 6 weeks.
“I can use high FODMAP ingredients (like onion and garlic) if I remove them before eating.”
This depends. The fructans in onion and garlic are water soluble, and the FODMAPs will filter out into the surrounding liquid.
Instead, if you them in a fat source like olive oil, and remove before adding the rest of the ingredients, the FODMAPs won’t leak out into the pan.
References:
1. NIH
2. NIDDK
Join the conversation at https://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp