Celiac disease damages the small intestine. This digestive disorder is triggered by eating foods containing gluten. Gluten is a protein found naturally in wheat, barley, and rye, and is common in foods such as bread, pasta, cookies, and cakes. Many pre-packaged foods, lip balms and lipsticks, hair and skin products, toothpastes, vitamin and nutrient supplements, and, rarely, medicines, contain gluten.
Celiac disease can cause long-lasting digestive issues and can also affect the body outside the intestine. The disease is different from gluten sensitivity or wheat intolerance.
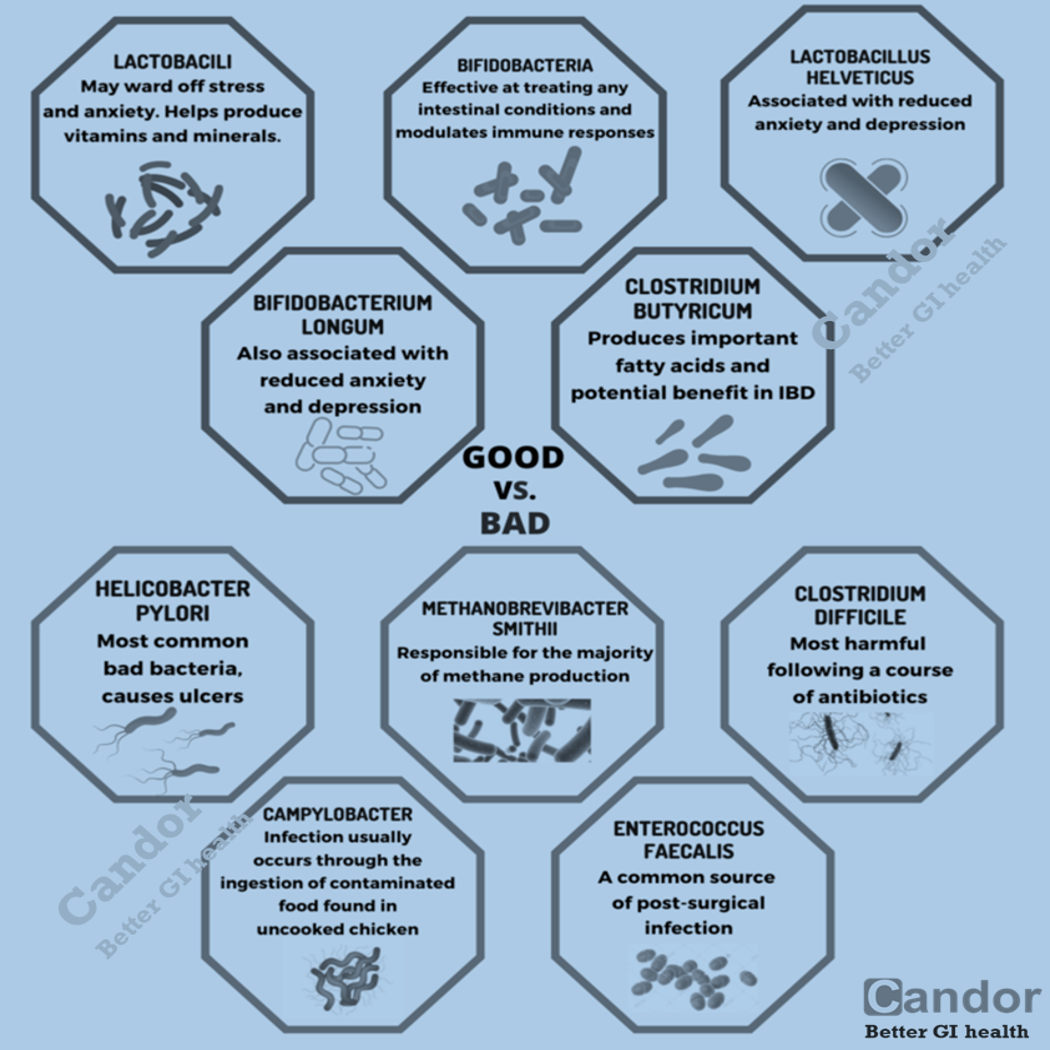
Gluten sensitivity symptoms may be similar to those of celiac disease, such as abdominal pain and tiredness but unlike celiac disease, gluten sensitivity does not damage the small intestine. Celiac disease is also different from a wheat allergy. In both cases, the body’s immune system reacts to wheat. However, some symptoms in wheat allergies, such as itchy eyes or breathing difficulties, are different from celiac disease. Wheat allergies also do not cause long-term damage to the small intestine.