What is a Low-FODMAP Diet?
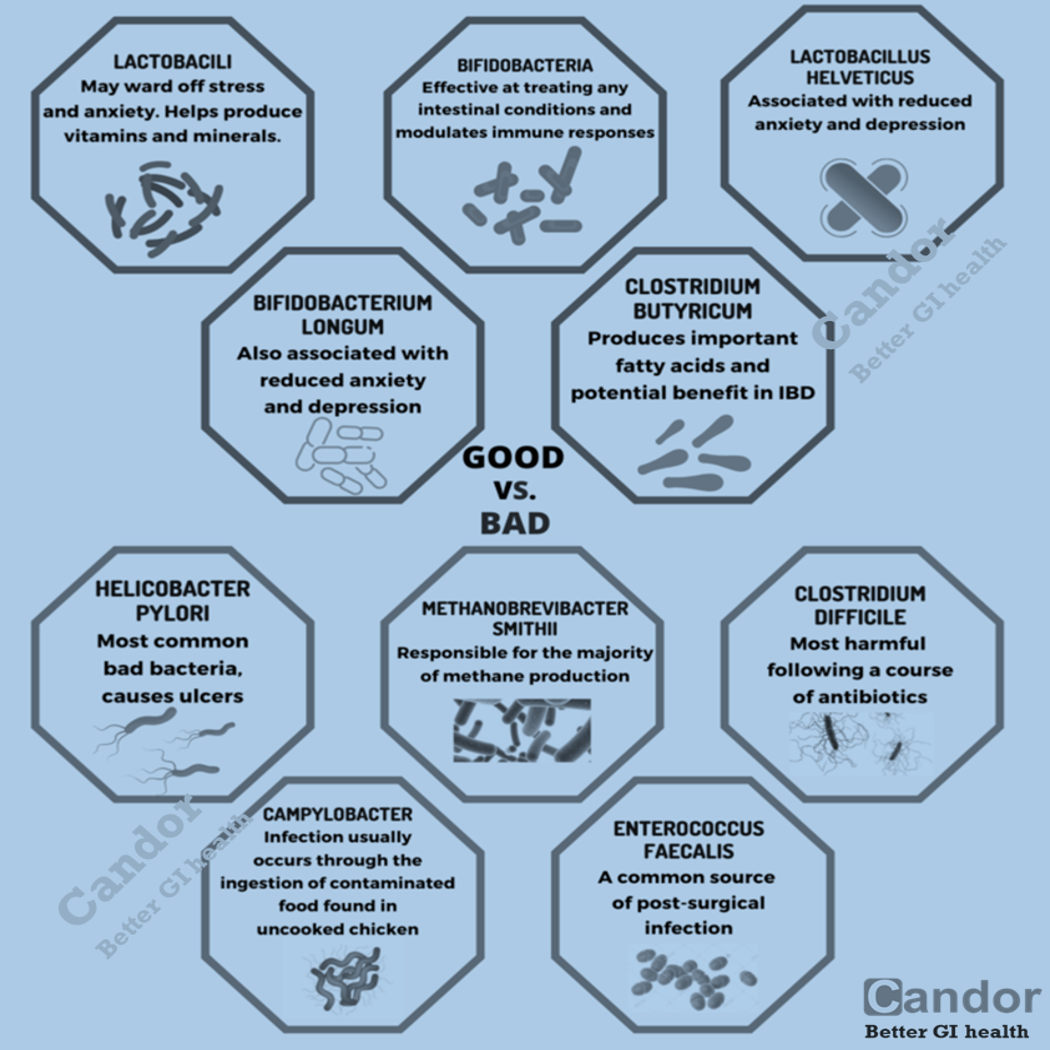
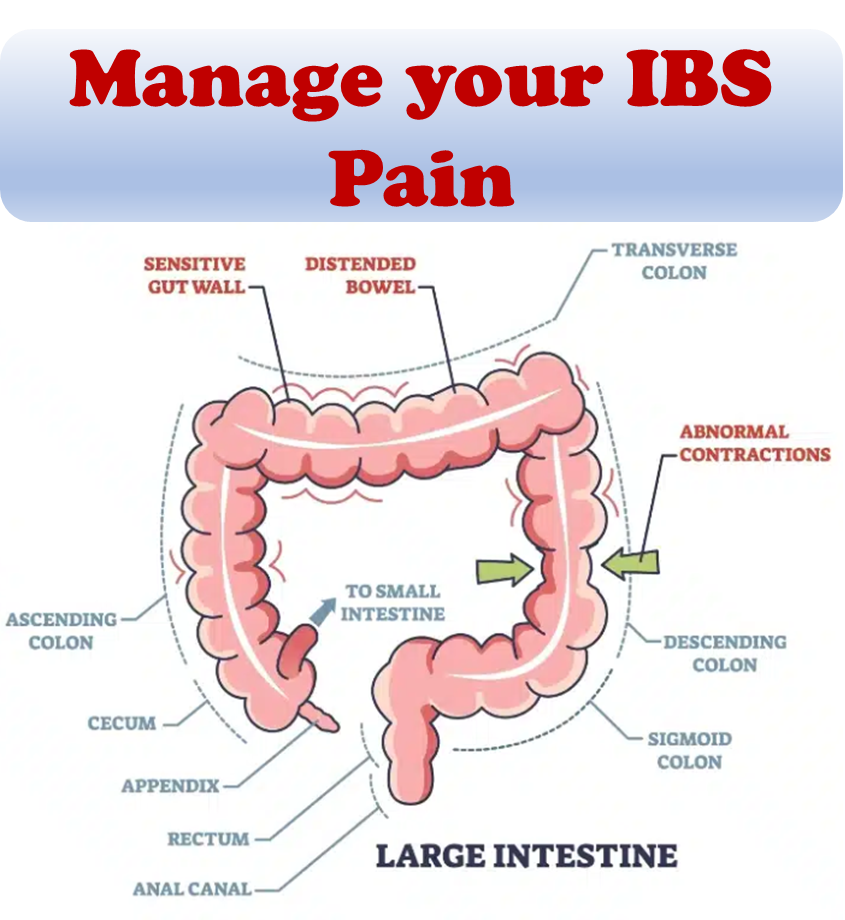
A low-FODMAP diet consists of the global restriction of all fermentable carbohydrates (FODMAPs), that is recommended only for a short time. A low-FODMAP diet is recommended for managing patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and can reduce digestive symptoms of IBS including bloating and flatulence.
Key Factors to Consider in Doing a Low-FODMAP diet:
A low-FODMAP diet might help to improve short-term digestive symptoms in adults with irritable bowel syndrome, but its long-term use can have negative effects because it causes a detrimental impact on the gut microbiota and metabolome. It should only be used for short periods of time and under the advice of a specialist.
The use of a this diet without medical advice can lead to serious health risks, including nutritional deficiencies and misdiagnosis, so it is advisable to conduct a complete medical evaluation before starting a low-FODMAP diet to ensure a correct diagnosis and that the appropriate therapy may be undertaken.
To learn more regarding the risks of a low-FODMAP diet, you can click here.
Since the consumption of gluten is suppressed or reduced with a low-FODMAP diet, the improvement of the digestive symptoms with this diet may not be related to the withdrawal of the FODMAPs, but of gluten, indicating the presence of an unrecognized celiac disease, avoiding its diagnosis and correct treatment.
A low-FODMAP diet is highly restrictive in various groups of nutrients, can be impractical to follow in the long-term and may add an unnecessary financial burden.
References:
1. National Institutes of Health (NIH)
2. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
Join the conversation at: https://www.facebook.com/getcandorapp