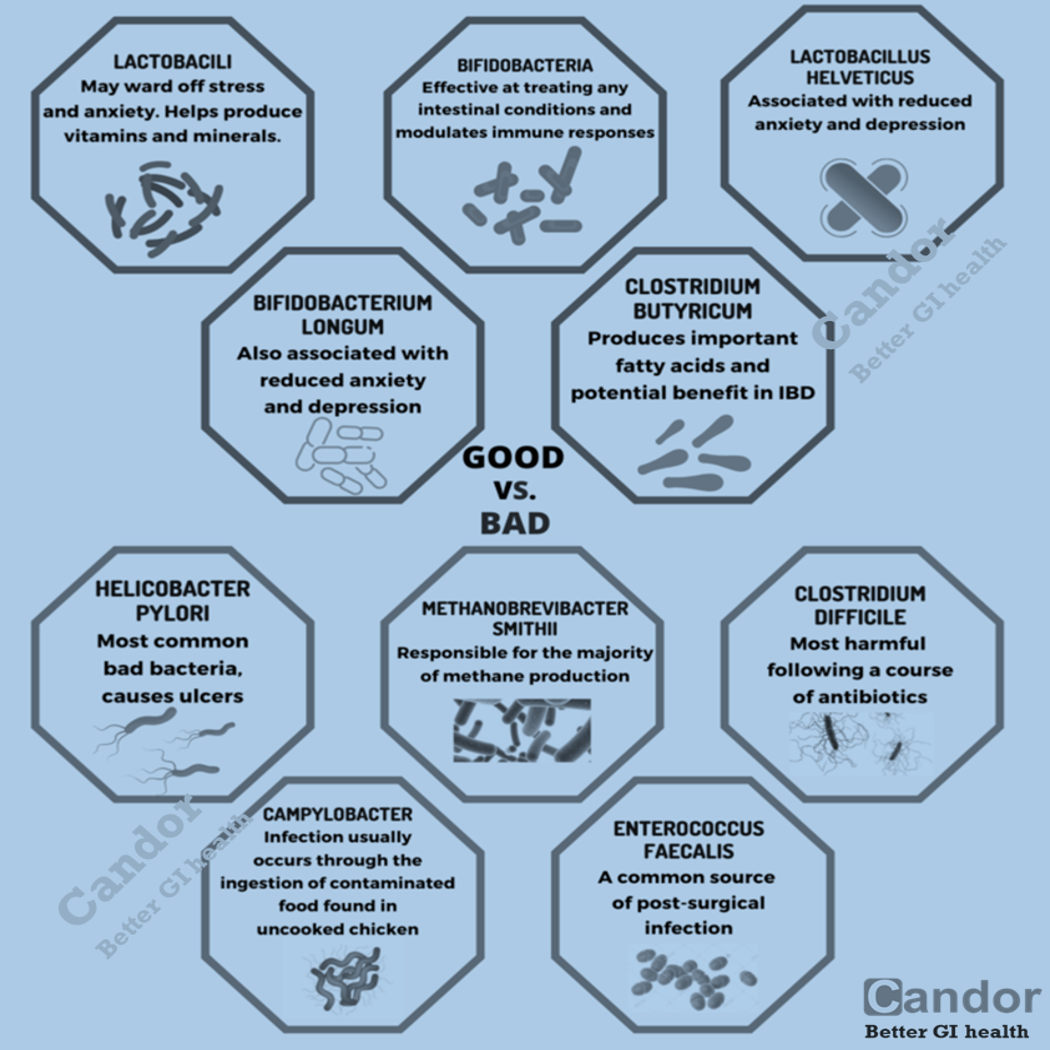
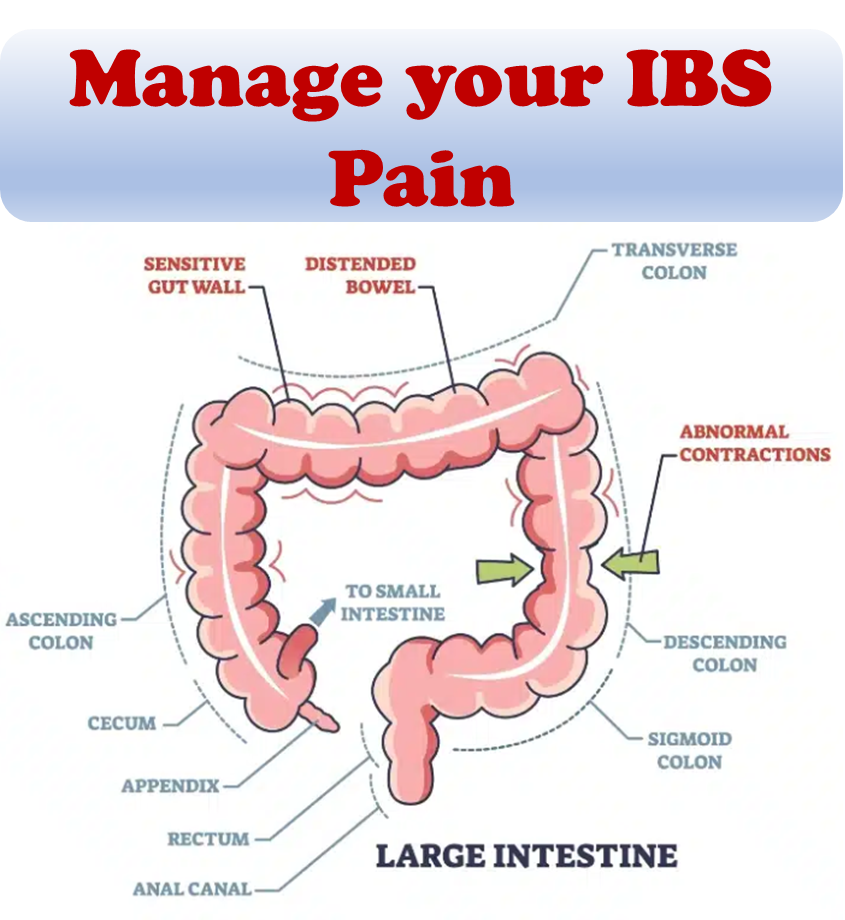
IBD and IBS are two illnesses that can affect the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Both can cause abdominal pain and changes in bowel movements. However, they are not the same. While there are many similarities between IBD and IBS, it is important to highlight the differences.
IBS:
- Functional GI disorder that causes recurrent abdominal pain and changes in bowel movements.
- Symptoms may include bloating, constipation, diarrhea, or mixed diarrhea with constipation.
- Patients with IBS have these symptoms without damage to the GI tract.
- Endoscopy and radiology tests do not show inflammation. Imaging (CT or MRI): No inflammation of the bowel wall seen typically.
IBD:
- Chronic inflammatory diseases involving the GI tract, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Immune cells cause inflammation and ulceration in the lining of the intestines, which can lead to frequent and/or urgent bowel movements, abdominal pain, diarrhea, or bleeding.
- In IBD, the GI tract is damaged. Symptoms can be different for everyone and depend on the type of IBD and where the inflammation is located in the GI tract.
- Endoscopy: redness, ulceration, bleeding seen with scope. Imaging (CT or MRI): inflammation of bowel wall is common.
References:
NIH, NIDDK