Not all Indian food is a potential trigger for your IBS symptoms. The impact of Indian food on triggering IBS flares can vary from person to person. Indian cuisine often includes a diverse range of ingredients, spices, and cooking methods, and not all dishes are necessarily triggers for IBS symptoms.
Some individuals with IBS may find that certain components commonly found in Indian food, such as spicy dishes, onions, garlic, and certain types of lentils or beans, can exacerbate their symptoms. These ingredients are known to be potential triggers for IBS symptoms in some people.
However, it is essential to recognize that not all Indian dishes are spicy or contain these specific ingredients. Indian cuisine also offers a variety of milder options, which may be better tolerated by individuals with IBS.
If you have IBS and enjoy Indian food, it’s advisable to be mindful of the ingredients and spices used in the dishes you choose. Keeping a food diary and noting how different foods affect your symptoms can help you identify potential triggers and make informed choices about your diet.
If you are uncertain about specific ingredients in a dish or have concerns about how it may affect your IBS, consider discussing your dietary preferences and concerns with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized guidance and help you create a diet plan that minimizes potential IBS triggers while still allowing you to enjoy the flavors of Indian cuisine.
When you think of “Indian food,” your mind might automatically conjure images of two things: curry and spicy dishes. However, Indian cuisine is far more diverse than that! While India is renowned as the “Land of Spices” and boasts a wide array of spice varieties, it does not mean that every Indian dish contains curry powder or is excessively spicy.
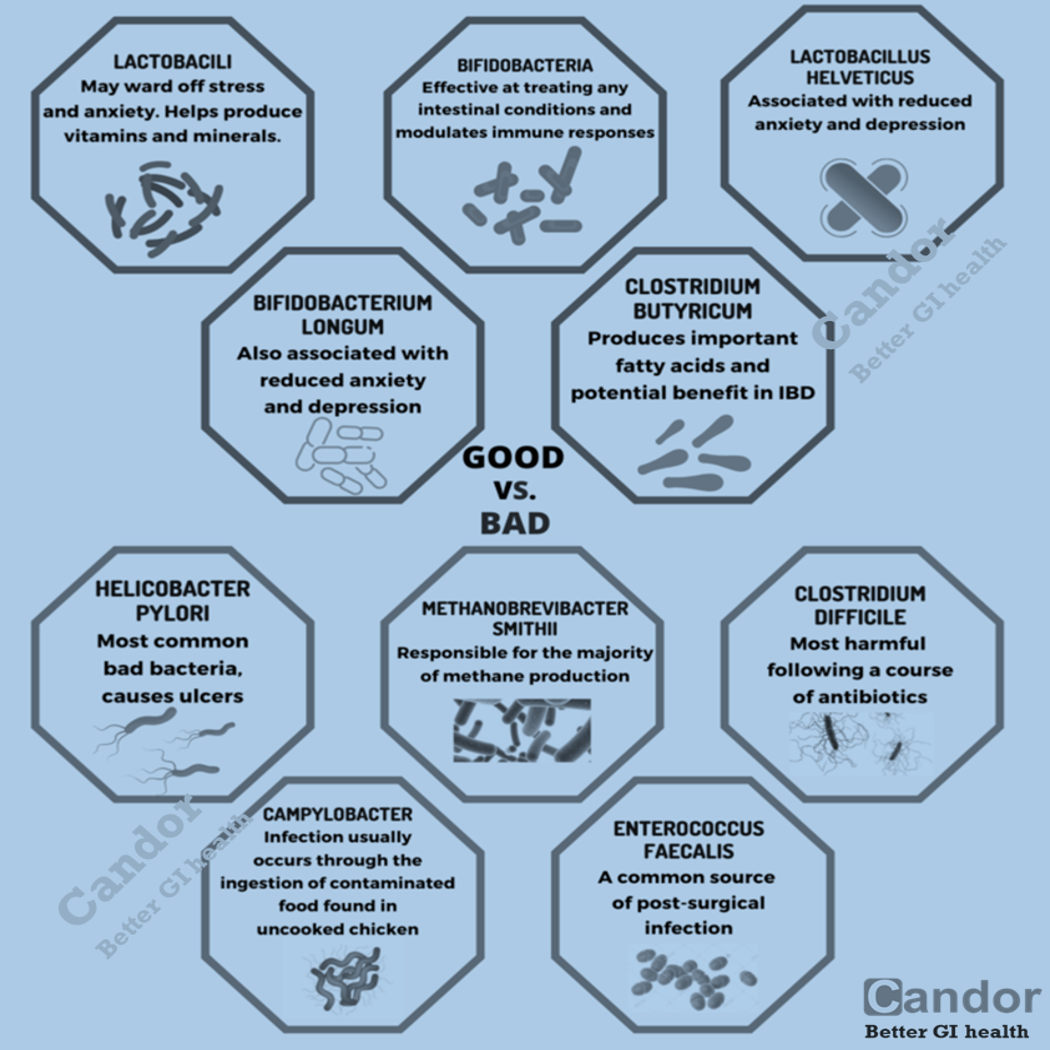
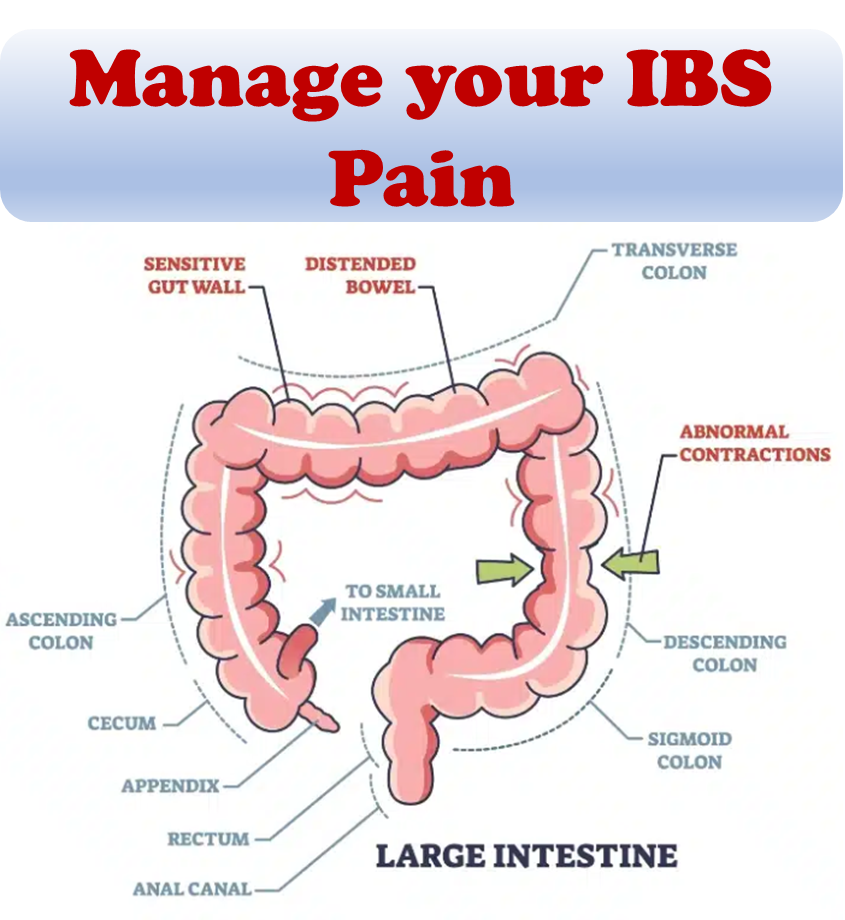
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a prevalent health condition characterized by symptoms like abdominal pain, acid reflux, bloating, constipation, diarrhea, and gas. Certain types of food, such as FODMAPs, fatty foods, and spicy dishes, have been associated with exacerbating these symptoms.
Due to misconceptions, some individuals with IBS avoid consuming Indian food altogether, believing that it universally contains curry or is excessively spicy. However, this broad generalization may prevent you from savoring some of the healthiest and most delectable dishes ever created!
So, is there a relationship between your IBS and Indian cuisine? The answer lies in the specific dishes you choose. Spicy food has been identified as a trigger for IBS symptoms, especially abdominal pain. If you adore Indian cuisine but suffer from IBS, fret not! You can still relish authentic and delicious Indian dishes without experiencing a major IBS episode. Instead of curry, opt for its milder counterpart, korma. Choose butter chicken or tandoori chicken in place of chicken tikka masala.
The realm of non-spicy Indian delicacies awaits you. Pakoras, papri chaats, and samosas are wholesome Indian snacks that won’t leave a burning sensation on your taste buds. Aloo paratha and dosa are flavorful Indian breads that offer both satisfaction and taste.
Many Indian dishes, particularly traditional ones, are prepared from scratch. This grants you complete control over the ingredients you incorporate into your meals, including the choice of spices and their quantities. This aspect makes Indian cuisine ideal for individuals seeking to customize their meals according to their dietary needs. Adjusting your Indian recipes to suit your preferences – such as using milder and sweeter curry powder to reduce spiciness – may be all you need to satisfy your craving for Indian food without enduring subsequent IBS symptoms.
References:
- “Definition and Facts for Irritable Bowel Syndrome”. NIDDKD. February 23, 2015.
- Chey WD, Kurlander J, Eswaran S (March 2015). “Irritable bowel syndrome: a clinical review”. JAMA.
- Whitehead WE, Palsson O, Jones KR (April 2002). “Systematic review of the comorbidity of irritable bowel syndrome with other disorders: what are the causes and implications?”. Gastroenterology.